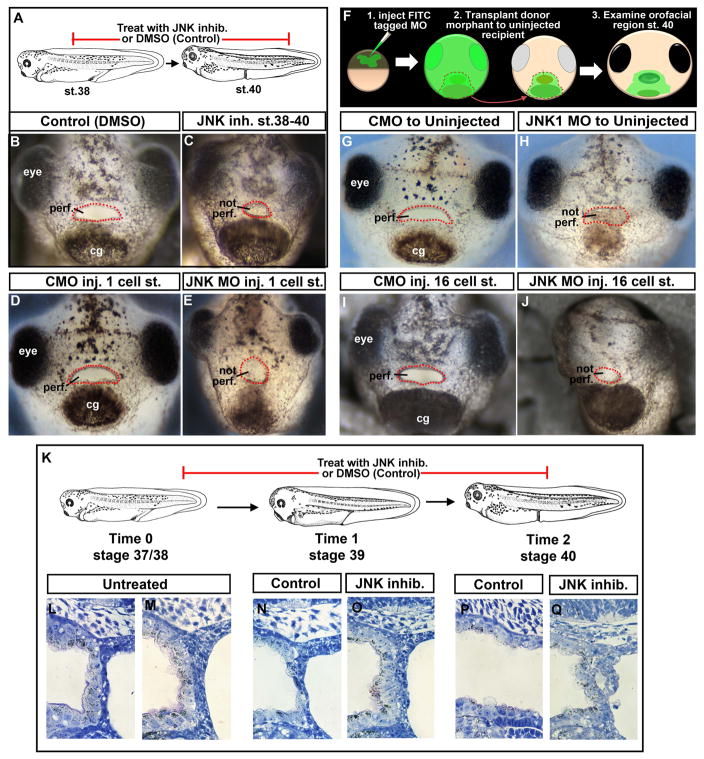
Figure 1.
A) Schematic showing treatment paradigm. B) Frontal view of a representative Control treated with 1% DMSO. C) Frontal view of a representative embryo treated with JNK inhibitor. D) Frontal view of a representative embryo injected with control morpholino at the 1 cell stage. E) Frontal view of a representative embryo injected with JNK1 morpholino at the 1 cell stage. F) Schematic showing face transplant paradigm. G) Frontal view of a representative control transplant. H) Frontal view of a representative embryo with JNK1 morphant tissue transplanted to its orofacial region. I) Frontal view of a representative embryo with control morpholino injected into D12 blastomere at the 16 cell stage. J) Frontal view of a representative embryo with JNK1 morpholino injected into D12 blastomere at the 16 cell stage. K) A schematic of the JNK inhibitor treatment paradigm and stages examined by histology. L, M) Shows sagittal sections through the buccopharyngeal membrane just prior to JNK inhibitor treatment at stage 37/38 (two representative images). N, O) Shows sagittal sections through the buccopharyngeal membrane at stage 39 in controls (N) and JNK inhibitor treated (O). P, Q) Shows sagittal sections through the buccopharyngeal membrane at stage 40 in controls (N) and JNK inhibitor treated. Abbreviations: perf. =perforated; cg=cement gland, inj. = injected, MO=morpholino, st. = stage. Red dots outline the embryonic mouth.