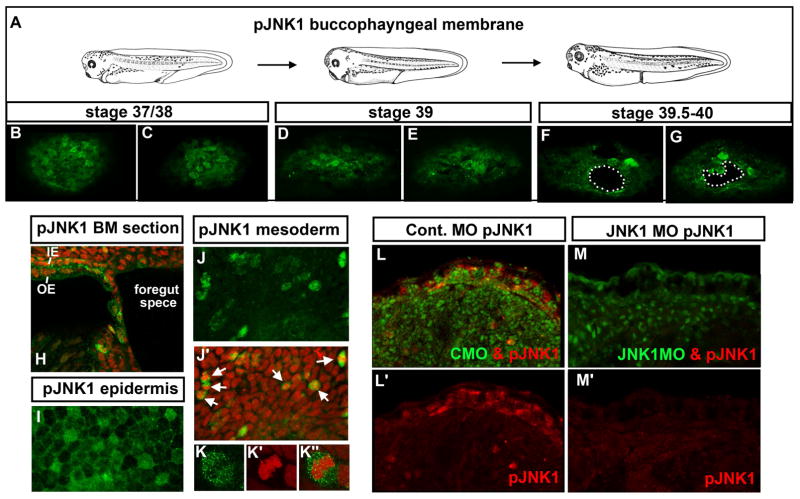
Figure 2.
A–G) Frontal views of the buccopharyngeal membrane labeled with pJNK1 antibody (green) at three different stages representing prior to and during perforation. White dots outline “holes” or perforations. H) Sagittal section through the buccopharyngeal membrane and surrounding face showing pJNK (green) and counterstained with propidium iodide. pJNK can also be observed in the two layered epidermis, in the outer epidermis (OE) and inner epidermis (IE). I) Flat mount of the epidermis labeled with pJNK antibody (green). J) The mesoderm labeled with pJNK antibody (green). J′) Corresponding image to J where the pJNK is labeled green and nuclei/DNA labeled with propidium iodide (red). White arrows indicate examples of cells that appear to be undergoing mitosis. K) Magnified image of a mesodermal cell labeled with pJNK antibody (green) K′) corresponding cell from K labeled with propidium iodide to show DNA (red). K″) Cell corresponding to K showing a merge of pJNK (green) and DNA (red). L) Embryos labeled with pJNK antibody (red) and showing the fluorescein tagged control morpholino (green). L′) Same image as L showing only the pJNK labeling (red). M) Embryos labeled with pJNK antibody (red) and showing the fluorescein tagged JNK1 morpholino (green) M′) same image as H showing only the pJNK labeling (red). Abbreviations: pJNK1=phospho JNK1, st. =stage.