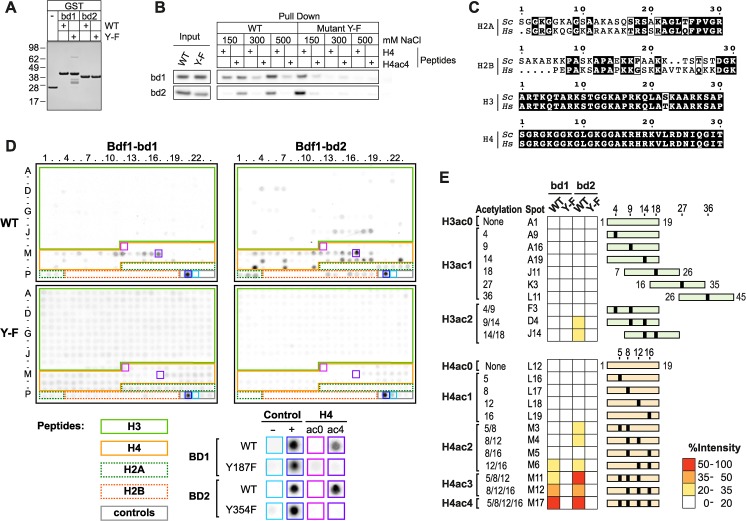
Fig 1. Bdf1 bromodomains bind multi-acetylated H4 tail.
(A) Purified Bdf1 bromodomains (Coomassie stained gel). Wild-type (WT). Mutations are Y187F and Y354F for Bdf1 bromodomain 1 and 2, respectively. (B) Pull-down assay using histone H4 (H4) and tetra-acetylated H4 peptides (H4K5ac K8ac K12ac K16ac, H4ac4). (C) Sequence alignment of the N-terminal sequences of H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 from human (Hs) and S. cerevisiae (Sc). (D) Binding profiles on a histone peptide array for WT and Y-F mutant of Bdf1 bromodomains. Control, H2A, H2B, H3 and H4 peptides are highlighted in grey, dashed green, dashed orange, plain green, plain orange, respectively. Signal for background, positive control, H4ac0 and H4ac4 peptides are highlighted on the array and shown at a higher magnification below the array. Signal intensity data can be found in S1 Table. (E) Bdf1 bromdomain binding intensities for a selection of H3 and H4 peptides. Acetylated sites are represented by black boxes on green (H3) or orange (H4) rectangles.