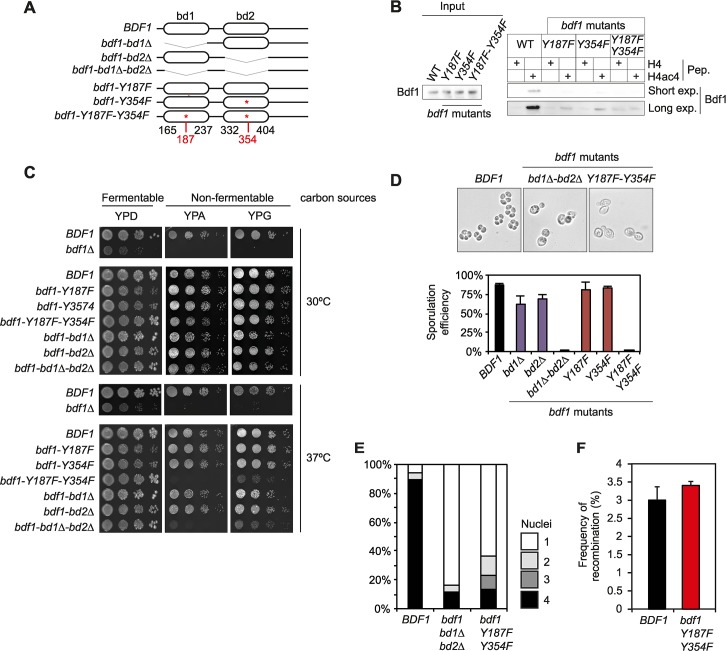
Fig 2. Bdf1 bromodomains are essential for sporulation.
(A) Schematic representation of the different bdf1 mutants. Bromodomains were deleted or mutated individually or in combination. Limits of bromodomains were based on [8]. Point mutations are identical to those used in Fig 1. (B) Pull-down analysis on H4 peptides (H4K5ac K8ac 12ac 16ac, H4ac4) using whole cell extracts from different bdf1 mutant strains. Bdf1 was detected using an antiserum specifically developed for this study (S4A Fig). Two exposure times, short or long, are presented and labelled "Short Exp" and "Long Exp", respectively. (C) Growth assay with bdf1 mutants on fermentable (glucose, YPD) and non-fermentable carbon sources (acetate or glycerol, YPA or YPG respectively). Assays were performed at two temperatures, 30°C and 37°C. (D) Sporulation efficiency of the Bdf1 bromodomain mutants. Mutation of both bromodomains of Bdf1 hampers the formation of spores (top). Quantification of sporulation efficiency (bottom). (E) Analysis of meiotic divisions by DAPI staining in bdf1 mutant strains. (F) Analysis of meiotic recombination in the bdf1-Y187F-Y354F mutant using the heteroalleles his4N / his4G.