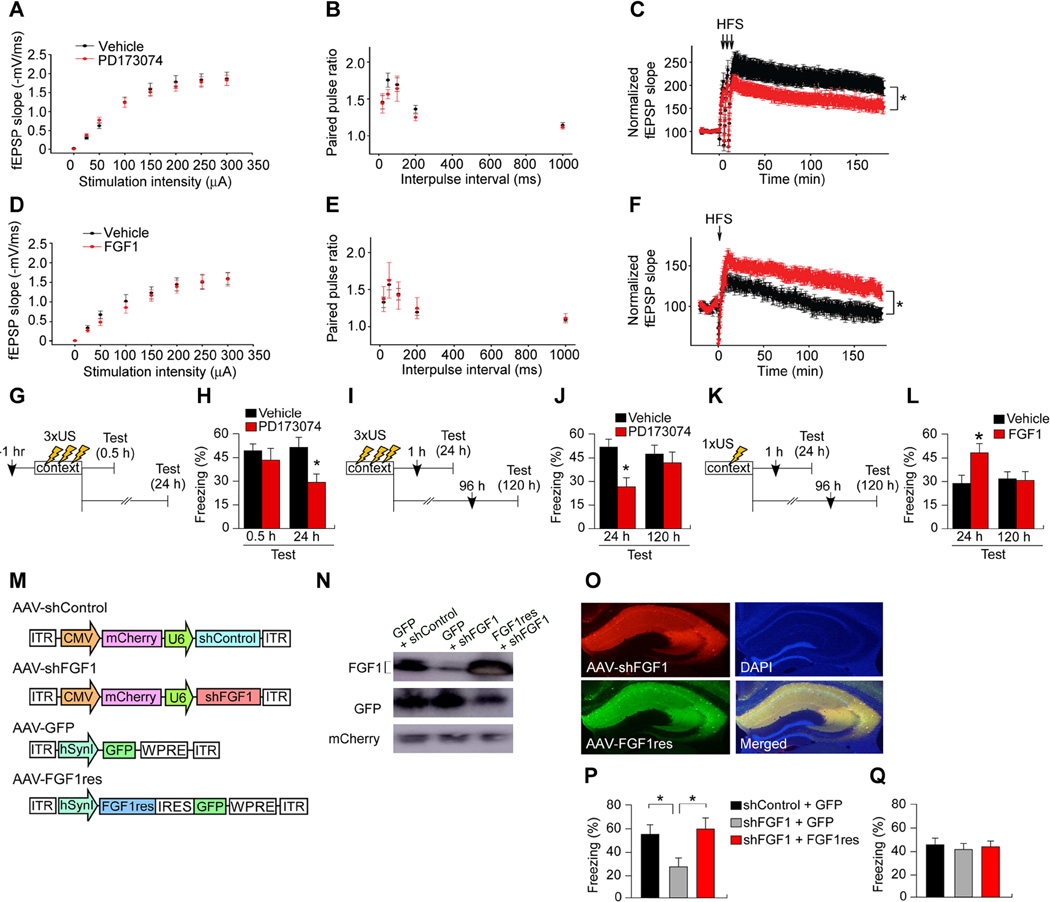
Figure 2. FGF1 is required for long-term potentiation and memory enhancement.
(A–C) Effect of the FGF receptor antagonist PD173074 on (A) input-output relationship (fEPSP slope in response to 50 µA–300 µA synaptic stimulations), (B) paired pulse ratio, and (C) 3 × HFS-evoked LTP at CA3-CA1 synapses. HFS: high frequency stimulation. Vehicle, 26 slices; PD173074, 30 slices. *p < 0.05.
(D–F) Effect of recombinant FGF1 on (D) synaptic the input–output relation, (E) paired pulse ratio, and (F) weak stimulus (1 × HFS)-evoked LTP. Vehicle, 11 slices; FGF1, 9 slices. *p < 0.05.
(G and H) Effect of PD173074 pretreatment on contextual fear memory (CFM). n = 13 or 14 per group. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group.
(I and J) Effect of PD173074 post-treatment on strong CFC training. n = 13 or 14 per group. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group.
(K and L) Effect of recombinant FGF1 post-treatment on weak CFM training. n = 12 or 13 per group. *p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated group.
(M) AAV vectors engineered to overexpress shRNA targeting Fgf1 (AAV-shFGF1), mock control (AAV-shControl), GFP (AAV-GFP), or shRNA-resistant Fgf1 (AAV-FGF1res).
(N) Western blot showing knockdown of FGF1 by AAV-shFGF1 and rescue by AAV-FGF1res in CA.
(O) Successful transduction of mCherry and GFP in CA region by AAV vectors. Scale bar, 1 mm.
(P) Mice co-injected with AAV-shFGF1 and AAV-GFP showed decreased long-term (24 h) CFM following 3-shock CFC. This reduction was not observed in mice co-injected with AAV-shFGF1 and AAV-FGF1res. n = 14–16 per group. *p < 0.05.
(Q) Mice injected with the viruses described in panel (P) showed normal short-term (1 h) CFM following 3-shock CFC. n = 10–13 per group.
Data presented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S2.