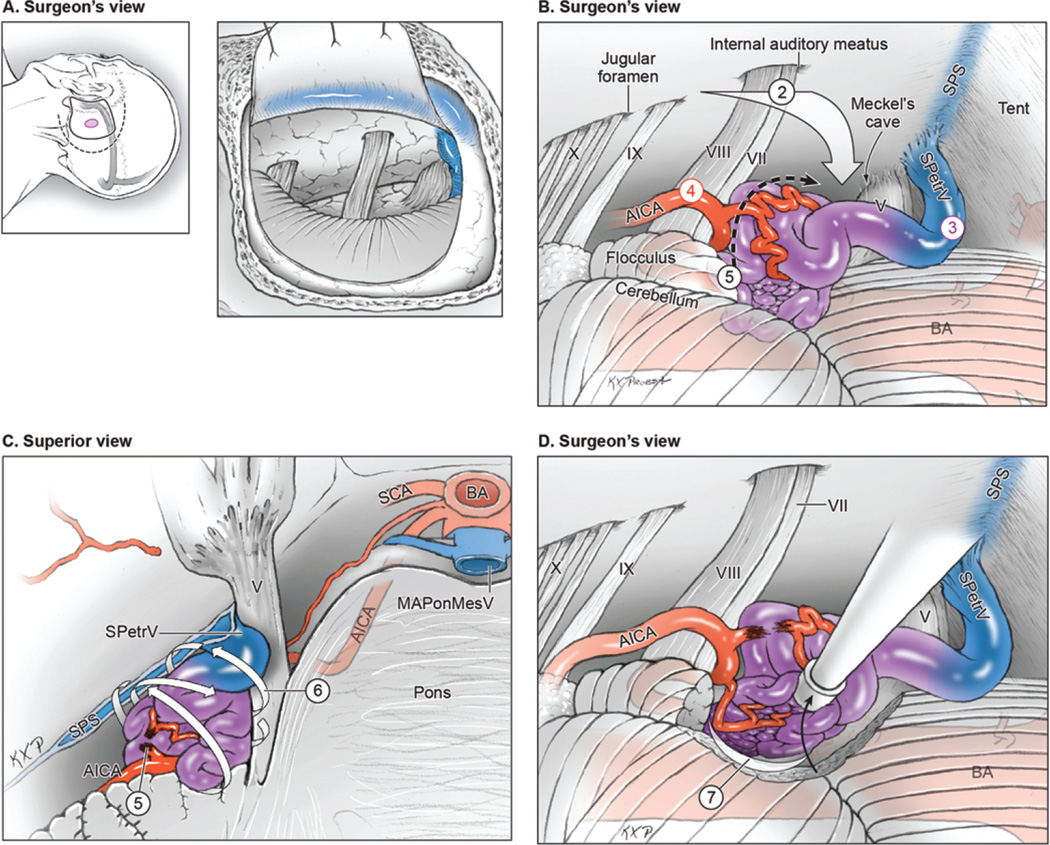
FIG. 2.
Surgical approach for lateral pontine AVMs. A: Step 1, exposing the AVM with an extended retrosigmoid approach that includes limited mastoidectomy and skeletonization of the sigmoid sinus (surgeon’s view, with scalp incision [dashed line], craniotomy [solid line], and AVM [purple circle] shown on the left and a dural flap mobilizing the skeletonized sigmoid sinus anteriorly shown on the right). B: Step 2, approaching the AVM through the cerebellopontine cistern; Step 3, identifying ascending drainage laterally (SPetrV); Step 4, locating AICA feeders in the infratrigeminal triangle; and Step 5, interrupting the medial front between the trigeminal and vestibulocochlear nerves (surgeon’s view). C: Step 6, circumdissecting the lateral, superior, and inferior margins in the cerebellum (back-door technique, superior view of the pons and posterior fossa). D: Step 7, mobilizing the AVM anteriorly to dissect the posterior plane along the brachium pontis and the medial plane along the pons (surgeon’s view). BA = basilar artery. Reproduced with permission from Lawton: Seven AVMs: Tenets and Techniques for Resection, Thieme, 2014.