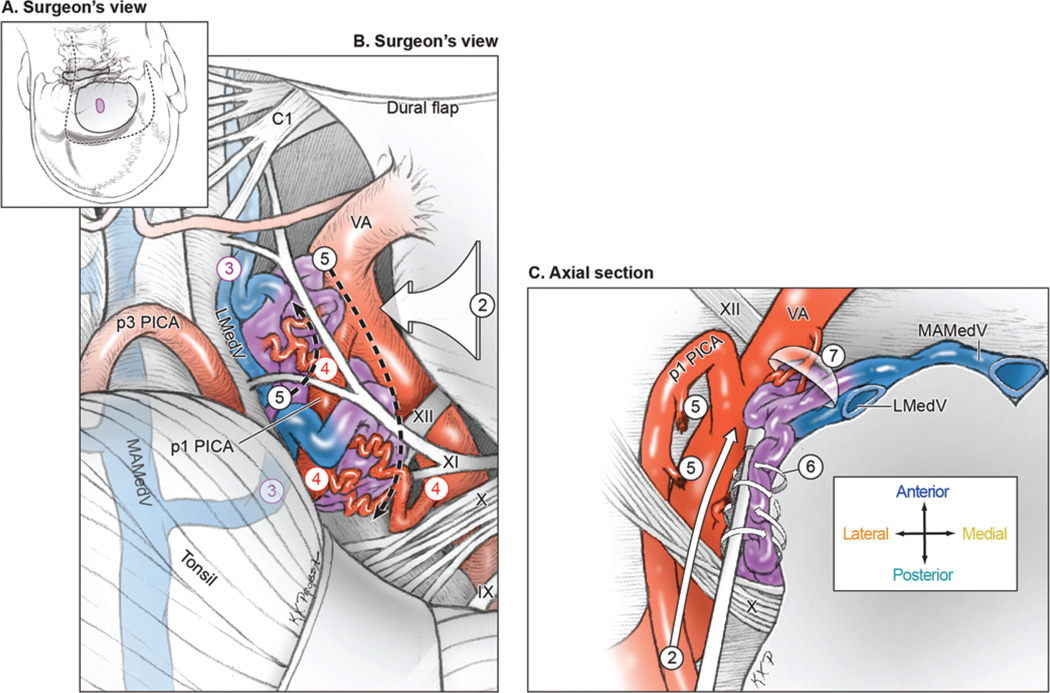
FIG. 4.
Surgical approach for lateral medullary AVMs. A: Step 1, exposing the AVM with a far-lateral craniotomy (surgeon’s view, with the patient in the park-bench position). Shown are the scalp incision (dashed line), craniotomy (solid line), and AVM (purple circle). B: Step 2, opening the cisterna magna and dissecting the vagoaccessory, suprahypoglossal, and infrahypoglossal triangles; Step 3, identifying the lateral draining vein (LMedV); Step 4, locating feeding arteries from the VA and PICA; and Step 5, skeletonizing the VA and PICA to interrupt the lateral front while preserving distal flow (surgeon’s view). C: Step 6, circumdissecting in the cerebellomedullary cistern and along the pial margin; and Step 7, mobilizing the AVM medially away from the VA to interrupt deep arterial connections and visualize anterior drainage to the MAMedV (axial cross-sectional view). Reproduced with permission from Lawton: Seven AVMs: Tenets and Techniques for Resection, Thieme, 2014.