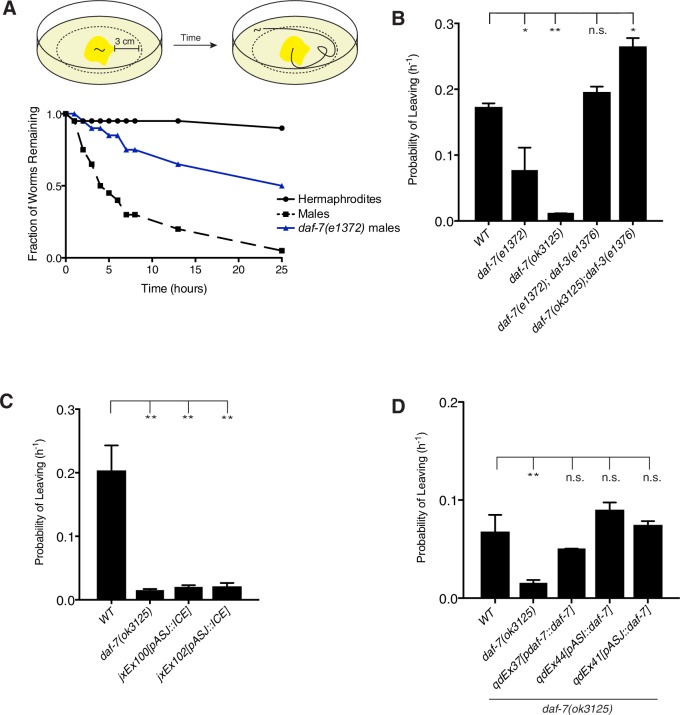
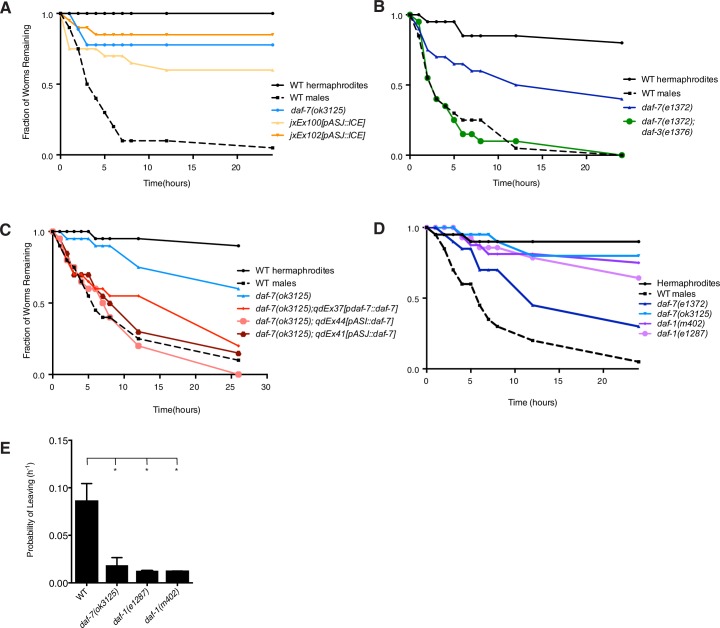
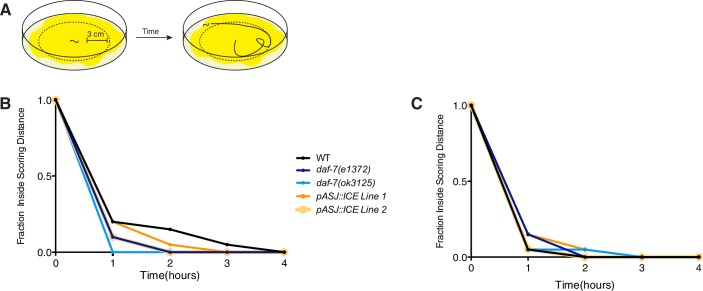
Figure 3. DAF-7/TGF-β is required for male mate-searching behavior.
(A) Schematic of mate-searching assay (top). Animals are placed individually into the center of a lawn of bacteria. The tracks of the animal are followed over time and scored for movement beyond 3 cm away from the food source. A representative data curve is shown on the bottom depicting hermaphrodites (solid black), males (dashed black), and daf-7(e1372) mutant males (blue). (B) Probability of leaving values for WT, daf-7 mutant, and daf-7;daf-3 double mutant males. Values plotted are the average + SEM for two independent experiments, n = 40 animals for all strains except daf-7(ok3125) where n = 29. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 as determined by ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. n.s., not significant. (C) Probability of leaving values for two independent lines of male animals with genetic ablation of the ASJ neurons, compared with corresponding values for WT and daf-7 mutant males. Values plotted are the average + SEM for two independent experiments for daf-7 mutant animals and three independent experiments for WT control and ASJ ablation strains. n = 60 animals for all strains except daf-7(ok3125) where n = 29 animals. **p<0.01 as determined by ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. One replicate was performed with the daf-7;daf-3 double mutant strains in 1B and controls (WT and daf-7) are identical, so probability values for that experiment were used in the averages shown in both B and C of this figure. (D) Probability of leaving values for daf-7(ok3125) mutant animals carrying transgenes expressing daf-7 cDNA specifically under the control of the indicated promoters. Values on graph are the average + SEM of two independent experiments with an n = 40 total animals for each strain. **p<0.01 as determined by ordinary one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. n.s., not significant.