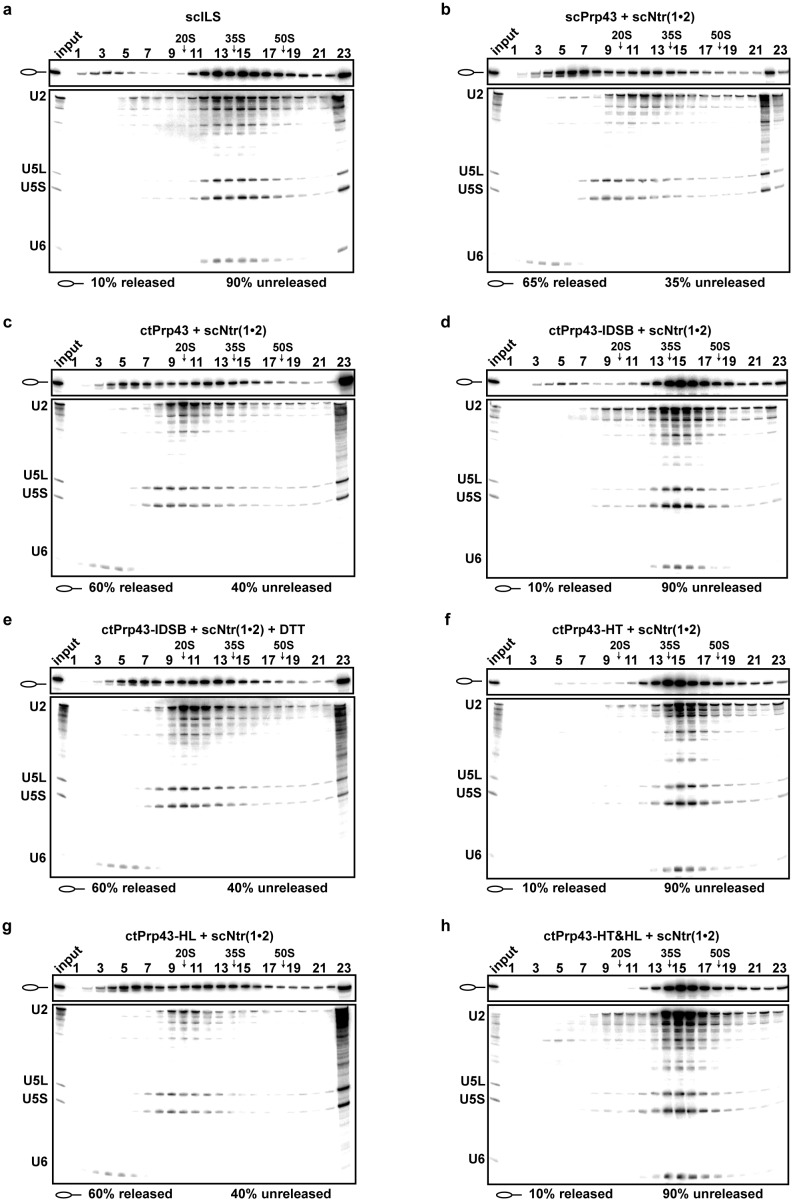
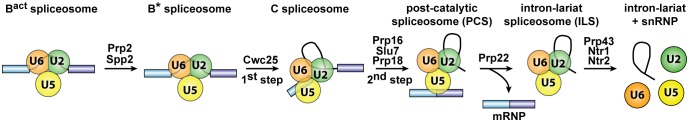
Figure 5. Intron-lariat spliceosome (ILS) disassembly assays.
10–30% glycerol gradient sedimentation of purified yeast ILS (scILS) incubated in solution with ATP plus (a) no recombinant protein, (b) scPrp43 and cofactors scNtr(1•2), (c) ctPrp43 and scNtr(1•2), (d) ctPrp43-IDSB and scNtr(1•2), (e) ctPrp43-IDSB, scNtr(1•2) and 0.5 mM DTT, (f) ctPrp43-HT and scNtr(1•2), (g) ctPrp43-HL and scNtr(1•2), (h) ctPrp43-HT&HL and scNtr(1•2). U2, U5 and U6 snRNAs were visualized by Northern blotting followed by autoradiography. RNA identities are indicated on the left. Quantifications were performed with ImageQuant software (Molecular Dynamics). Numbers represent the percentage of intron-lariat RNA released in the top fractions (sum of fractions 1–11) or associated with the ILS (unreleased, sum of fractions 12–23) relative to the intron-lariat RNA distributed in all 23 fractions, the sum of which was set to 100%.