Fig. 6. KDM5s are involved in selection of polyA sites.
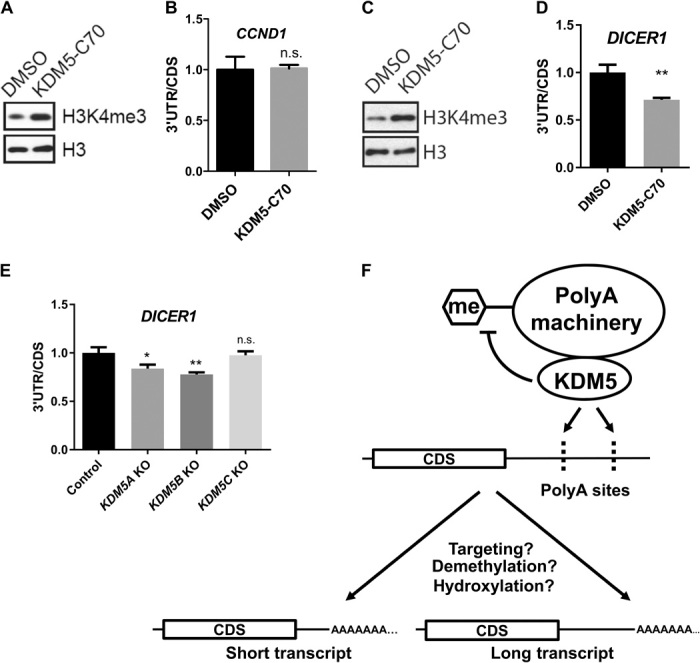
(A) Western blot and (B) RT-qPCR analyses of MCF7 cells treated with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or 10 μM KDM5-C70 for 3 days. The ratio of 3′UTR to CDS for CCND1 mRNA was plotted. Error bars represent SEM for biological triplicate experiments. (C) Western blot and (D) RT-qPCR analyses of HeLa cells treated with DMSO or 10 μM KDM5-C70 for 3 days. The ratio of 3′UTR to CDS for DICER1 mRNA was plotted. Error bars represent SEM for biological triplicate experiments. **P < 0.01. (E) RT-qPCR analysis of HeLa/iCas9-c1 cells transduced with lentiviruses carrying single-guide RNAs against KDM5A, KDM5B, KDM5C, or nontargeting control. The ratio of 3′UTR to CDS for DICER1 mRNA was plotted. KO, knockout. Error bars represent SEM for biological triplicate experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (F) Working model for KDM5 involvement in APA. KDM5 recruits the polyA machinery to nascent RNA to modulate polyA site choices. Demethylation or hydroxylation of certain subunits of the polyA machinery by KDM5 also contributes to selection of the polyA sites. The polyA sites (dashes) are noted on the nascent transcript.
