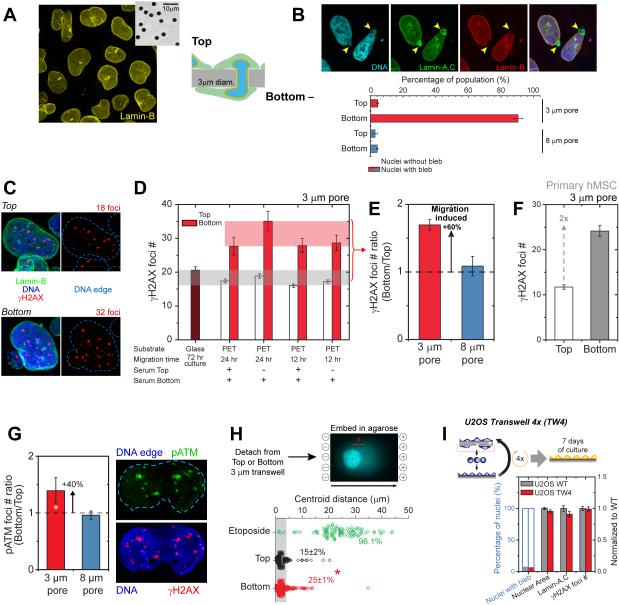
Figure 1. Migration through 3-μm pores causes transient nuclear lamina rupture and DNA breaks, and repair factor mis-localization.
(A, B) U2OS nuclei on tops of transwells are rounded (inset: 3-μm pores). Migration elongates and causes blebs on poles but not with 8-μm pores (Figure S1; ≥40 nuclei per condition, n≥3 expts).
(C-F) Immunostained γH2AX foci on tops and bottoms of transwells (polyester, PET) or glass show increased damage after U2OS migration thru 3-μm but not 8-μm pores. Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) show more foci after 3-μm pore migration (Figure S1; ≥45 nuclei per condition, n=3 expts, *p<0.05).
(G) Immunostained phospho-ATM (pATM) foci show increased damage after U2OS migration thru 3-μm but not 8-μm pores (≥50 nuclei per condition, n≥3 expts, *p<0.05).
(H) Comet assay for DNA breaks in isolated U2OS nuclei show 3-μm pore migration causes more centroid shifts (threshold: 3-μm) as does Etoposide in cultures (10μM, 2hrs). (≥175 nuclei per group, n≥3 expts, *p<0.05).
(I) Post-migration recovery of lamin-A,C, DNA damage, nuclear area, and blebs. (≥130 nuclei per condition, n≥3 expts).