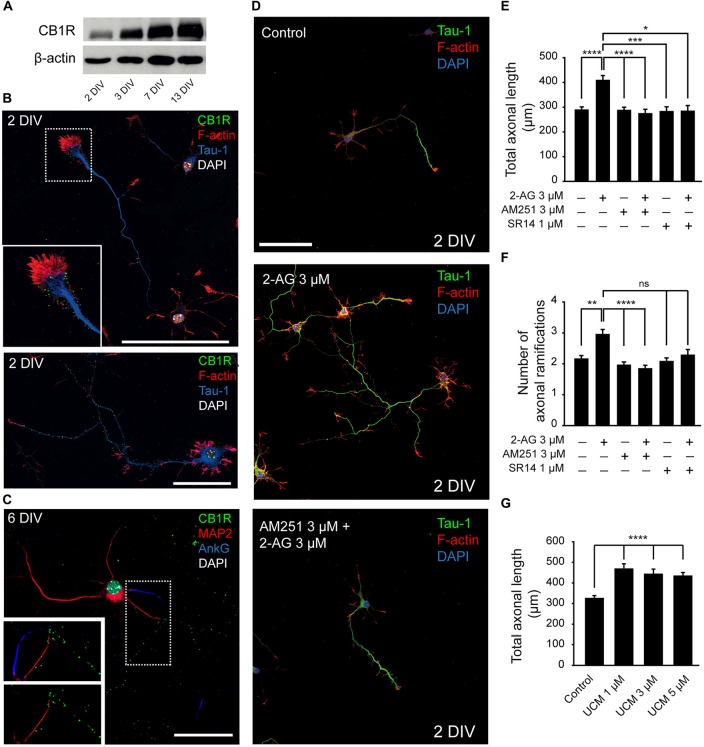
Figure 1.
Modulation of axonal growth by the type-1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1R). (A) Western-blot showing CB1 receptor total expression levels on 2, 3, 7 and 13-days in vitro (DIV) hippocampal neurons. (B) CB1 receptor (green) expression in 2-DIV hippocampal neurons. Growth cones are stained with phalloidin-Alexa 594 (red), axons with Tau-1 antibody (blue) and nuclei with DAPI (white). The inset shows a magnification of the growth cone region. Note that CB1 receptors show a punctate staining and are mainly concentrated in the axonal growth cone and along the axonal shaft (image below). (C) CB1 receptor (green) expression in 6-DIV hippocampal neurons. CB1 receptors are expressed along the axon and are not detected by immunofluorescence in the dendrites (red) or the axon initial segment (AIS; blue). Magnification of the image is shown below with or without AIS marker staining (AnkyrinG, blue). (D) 2-DIV hippocampal neurons treated with 2-Arachidonylglycerol (2-AG) or 2-AG in combination with AM251 from plating until 2 days. Neurons were stained using a Tau-1 antibody and Phalloidin for better recognition of neuronal and axonal morphology. Scale bar = 100 μm. (E–G) Bar plots representing the mean ± SEM of axonal length or total number of axonal ramifications of 2-DIV hippocampal neurons treated with CB1R antagonists, and/or agonist (E,F) or treated with monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) inhibitor UCM03025 (G). Data were acquired from three independent experiments (30 neurons/experimental condition in each experiment). Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. Adjusted p values: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001; ns, non-significant.