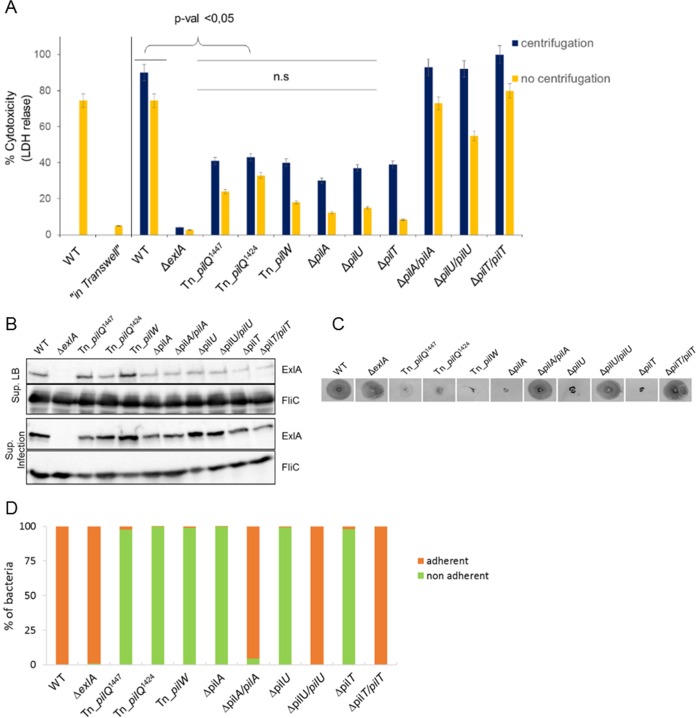
FIG 5 .
Type IV pili are required for ExlA-dependent cytolysis. (A) Cytotoxicity assays were performed using A549 cells and mutants identified during screening of a transposon (Tn) library, strains with engineered chromosomal deletions (ΔpilA, ΔpilU, and ΔpilT), and the complemented strains. The LDH release was measured as described in the Fig. 1 legend. Where indicated, infections were done in the Transwell system, where bacteria and A549 cells were separated with a membrane. Note the absence of LDH release for “in Transwell” conditions. When indicated, centrifugation was performed immediately after initiation of infection. Analysis of variance was used to compare pil mutants to WT (P ≤ 0.05; n.s., not significant). (B) Secretion of ExlA in pil mutants. Immunoblot analysis was performed using anti-ExlA and anti-FliC antibodies on proteins TCA precipitated from the LB growth medium (Sup. LB) or from cell culture medium following infection of A549 cells with the bacteria (Sup. Infection). (C) Twitching motility of IHMA (WT), IHMAΔexlA and pil mutants, and complemented strains, assessed by Coomassie blue staining of motility plates after 48 h. (D) Adhesion of P. aeruginosa IHMA, IHMAΔexlA and various pil mutants, and complemented strains to A549 cells, quantified after 30 min of infection by enumerating the bacteria (as CFU) in cell-associated (adherent) and supernatant (nonadherent) fractions.