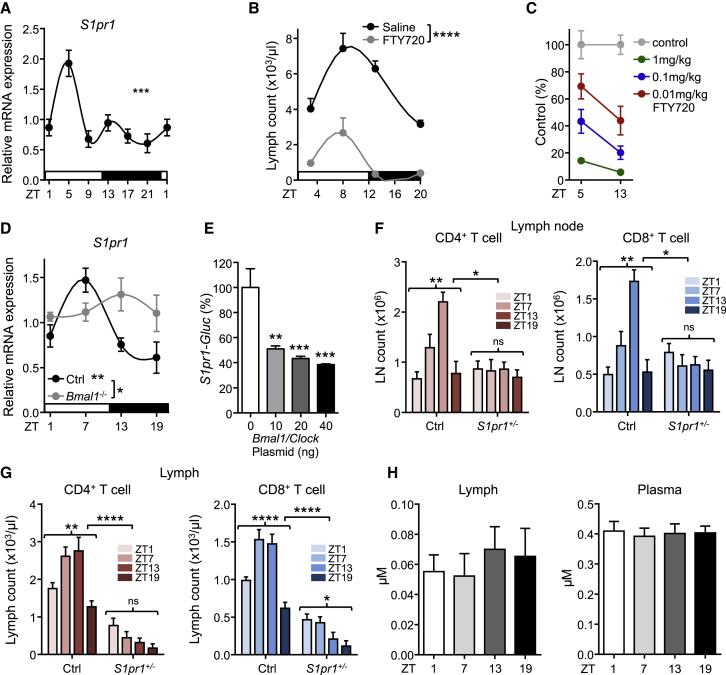
Figure 5.
Rhythmic Lymphocyte Egress Depends on Oscillatory S1pr1 Expression
(A) Q-PCR analysis of LN S1pr1 over 24h. n = 3–5 mice, one-way ANOVA.
(B) Lymph counts after blockade of S1P-receptor function using FTY720 at the indicated times; n = 3–33 mice, two-way ANOVA.
(C) FTY720 titration and respective lymph counts at two time points. n = 3–5 mice.
(D) Q-PCR analysis of CD4+ T cell S1pr1 over 24 hr in control and T cell-specific Bmal1−/− mice; n = 4–9 mice, one-way and two-way ANOVA.
(E) Normalized activity (in %) of Gaussia Luciferase driven by murine S1pr1 promoter (S1pr1-GLuc) after co-transfection with various doses of Clock and Bmal1 plasmids in HEK293 cells (n = 6). Data shown are pooled from two independent experiments, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.
(F) LN CD4+ and CD8+ T cell counts in control and T cell-specific S1pr1 heterozygous mice; n = 3–6 mice, one-way and two-way ANOVA.
(G) Lymph CD4+ and CD8+ T cell counts in control and T cell-specific S1pr1 heterozygous mice; n = 3–12 mice, one-way and two-way ANOVA.
(H) Mass spectrometric analysis of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) in lymph and blood plasma; n = 9–11 mice. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. All data are represented as mean ± SEM. See also Figure S5.