Figure 2.
GluA3 Is Required for PF-PC LTP, but Not LTD
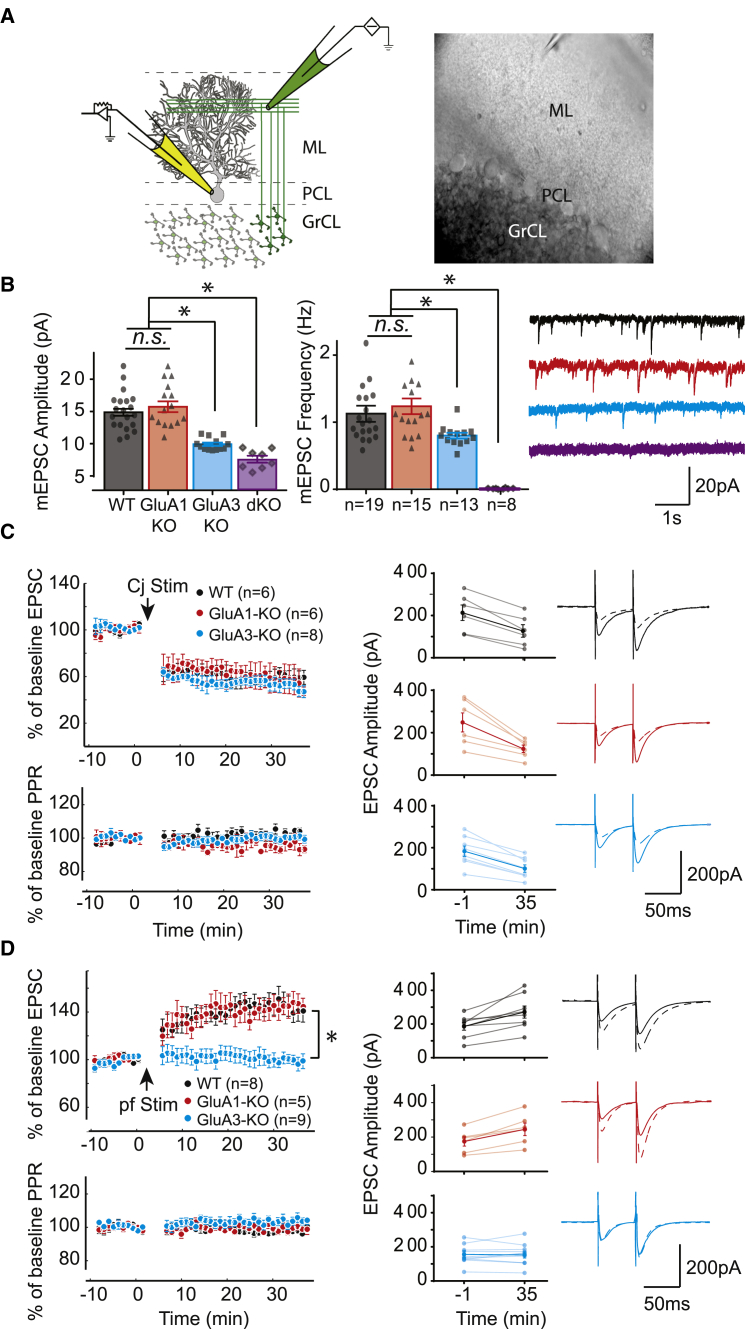
(A) Scheme of cerebellar cortical circuitry (left) and representative picture of the in vitro preparation (right) showing positions of recording electrode (yellow) at PC soma and stimulus electrode (green) at parallel fiber beam. ML, PCL, and GrCL indicate molecular layer, PC layer, and granule cell layer, respectively.
(B) mEPSC amplitude (left) and frequency (middle) of both single GluA3-KO PCs (blue bar) and double GluA1/GluA3-KO PCs (purple bar) were significantly reduced compared to those in WT PCs (black bar) (for amplitude and frequency, WT versus GluA3-KO, p = 0.0003 and p = 0.023, respectively; for WT versus GluA1&3-dKO, p < 0.0001 and p < 0.0001, respectively) and single GluA1-KO PCs (red bar) (for amplitude and frequency, GluA1-KO versus GluA3-KO, p < 0.0001 and p = 0.0032, respectively). In contrast, GluA1-KO and WT PCs presented comparable basal transmission (for amplitude and frequency, WT versus GluA1-KO, p = 0.37 and p = 0.16, respectively). Right panel shows corresponding raw traces of mEPSCs.
(C) Both GluA1-KO (red) and GluA3-KO (blue) mice show similar cerebellar synaptic weakening after LTD induction compared to WT littermates (black) (top left) with unchanged PPR over time (bottom left). EPSC magnitude was held in a comparable range for all cases to prevent potential bias due to differential basal synaptic strength (middle). Representative traces are of paired EPSCs before (solid lines) and after (dashed lines) LTD induction (right, matched genotype color code). Cj Stim indicates conjunctive stimulation (so as to induce LTD).
(D) GluA3-KO PCs show severe deficits in PF-PC LTP compared with WT and GluA1-KO PCs with no changes in PPR or baseline EPSC magnitude. Representative traces of paired EPSCs before (solid lines) and after (dashed lines) LTP induction (same configuration as in B). pf Stim indicates parallel-fiber-only stimulation (so as to induce LTP).
Error bars indicate SEM; ∗ indicates p < 0.05.