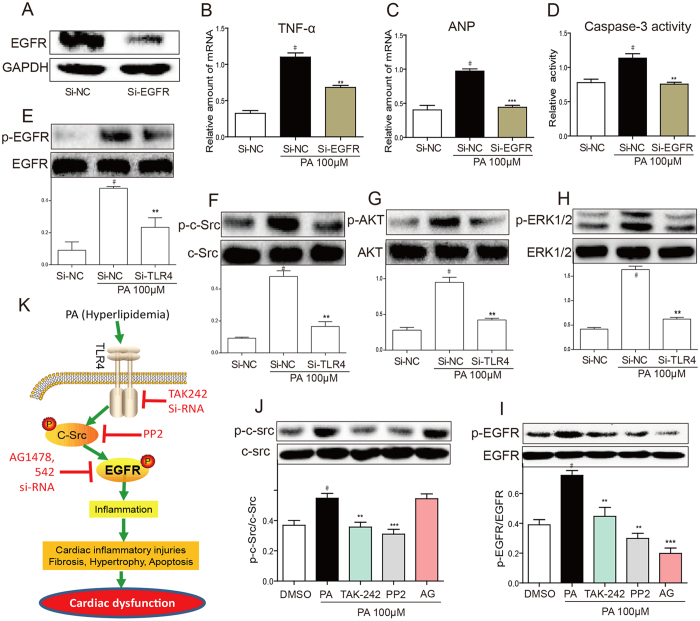
Figure 7. PA induces EGFR activation through TLR4/c-Src signaling cascade in H9C2 cells.
(A–D) EGFR siRNA attenuated PA-induced cell injury. H9C2 cells were pretreated with EGFR siRNA for 6 h, and the down-regulation of EGFR protein expression was determined by western blotting (A). A scrambled sequence for the EGFR siRNA was used as the negative control (si-NC). Similar results were observed in three independent experiments. After incubating for 24 h, EGFR-silencing H9C2 cells were stimulated with PA (100 μM) for 6 h. TNF-ɑ (B) and ANP (C) mRNA levels were measured by qPCR and normalized by β-actin. Bars represent the mean ± SD of four independent experiments run in triplicate. The intracellular caspase-3 activity was evaluated upon PA (100 μM) treatment for 24 h (D). (E–H) TLR4 siRNA inhibited PA-induced EGFR pathway activation. H9C2 cells were pretreated with siTLR4 for 6 h to knock down TLR4. The phosphorylation levels of EGFR (E), c-Src (F), AKT (G), and ERK1/2 (H) were determined by western blot method after PA (100 μM) treatment for 15 min. The column figure shows the normalized optical density from four independent experiments. (I,J) H9C2 cells were pretreated with TAK-242 (TLR4 inhibitor), or PP2 (c-Src inhibitor), or AG1478 for 1 h, followed by PA (100 μM) treatment for 15 min. Phosphorylation of EGFR (I) and c-Src (J) were determined by western blot analysis. The gels were run under the same experimental conditions. Shown are cropped gels/blots (The gels/blots of 7A,E–J with indicated cropping lines are shown in Supplementary Fig. S4). The column figure shows the normalized optical density from four independent experiments. Values are reported as means ± SEM (n = 4, #P < 0.05, vs. si-NC or DMSO group; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. PA treatment group). (K) A schematic illustration of the molecular mechanism underlying the protection of EGFR inhibitors against hyperlipidemia-induced lipotoxicity cardiomyopathy.