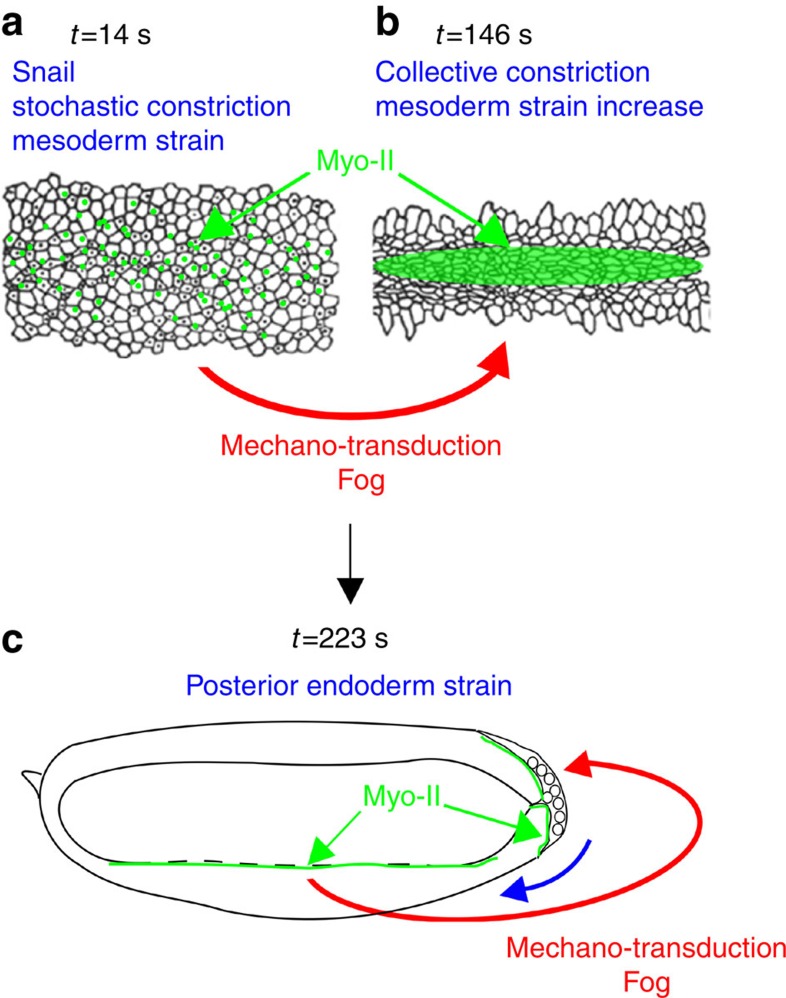
Figure 8. Meso-endoderm mechanotransductive cascade of Myo-II apical stabilization.
(a) Sna-dependent stochastic fluctuation of mesoderm apex size (b) activates the medio-apical accumulation of Myo-II in a Fog-dependent mechanotransductive process leading to coordinated collective constriction of the cell apex (initiating nearly 130 s after the initiation of pulsations), then mesoderm invagination. (c) In turn, mesoderm constriction generates a strain deformation of posterior endoderm cells (blue array) that activates the apical stabilization of Myo-II required for endoderm invagination nearly 80 s after mesoderm collective constriction initiation, that is subsequently reinforced during mesoderm invagination, in a Fog-dependent mechanotransductive pathway. Adapted from the figures of morphogenetic movements of Sweeton et al.,26 Development, 1991 and Nüslein-Volhard & Wieschaus, Drosophila a practical approach, 1896.