Figure 4.
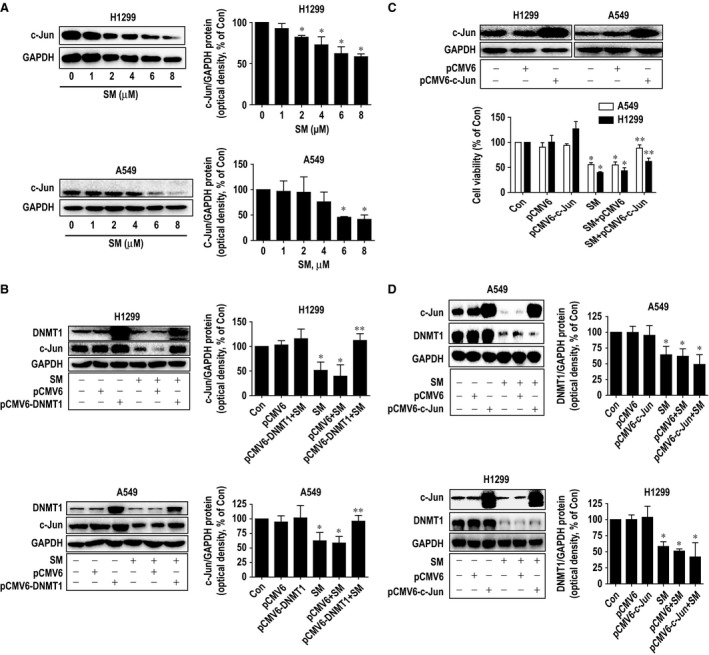
Solamargine inhibited c‐Jun protein through inhibition of DNMT1 expression; exogenously expressed c‐Jun resisted the solamargine‐inhibited cell growth. (A) A549 and H1299 cells were treated with increased concentration of solamargine for 24 hrs. Afterwards, the expression of c‐Jun protein was detected by Western blot. (B) A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with the control or expression construct of DNMT1 for 24 hrs before exposing the cells to solamargine (6 μM) for an additional 24 hrs. Afterwards, the expression of DNMT1 and c‐Jun proteins were determined by Western blot and was expressed as percentage of control in the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. GAPDH was used as internal control. (C) A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with the control or expression construct of c‐Jun for 24 hrs before exposing the cells to solamargine (6 μM) for an additional 24 hrs. Afterwards, the expression of c‐Jun protein and cell viability were determined by Western blot and MTT assays, respectively. GAPDH was used as internal control. Values in bar graphs were expressed as percentage of control in the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. (D) A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with the control or expression construct of c‐Jun for 24 hrs before exposing the cells to solamargine (6 μM) for an additional 24 hrs. Afterwards, the expression of DNMT1 and c‐Jun proteins were determined by Western blot and was expressed as percentage of control in the mean ± SD of three separate experiments. GAPDH was used as internal control. *Significant difference compared with the untreated control group (P < 0.05). **Significant difference from solamargine treated alone (P < 0.05).
