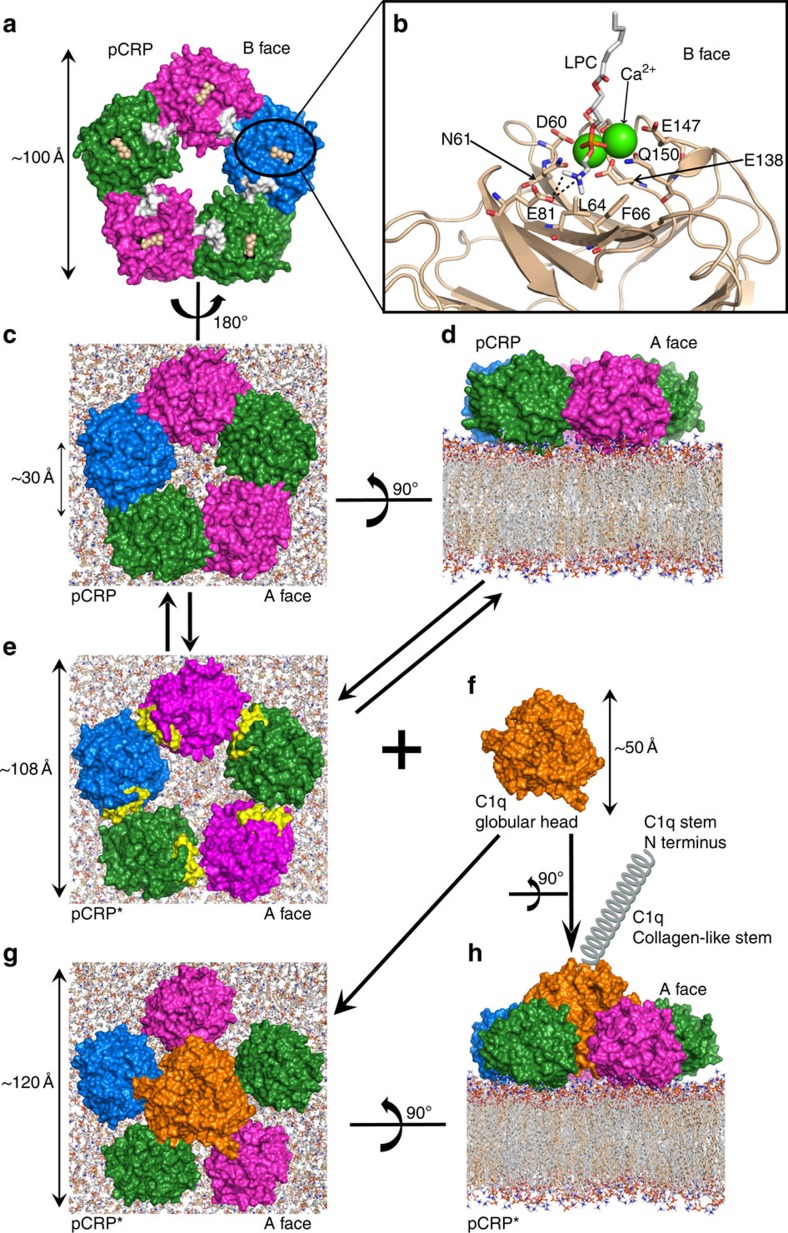
Figure 7. Model of the pCRP conformational rearrangement to pCRP* and interaction of pCRP* with complement C1q.
(a) The individual subunits of human pCRP (PDB ID: 1B09; ref. 7) have been displayed as a molecular surface and coloured to highlight the subunit boundaries. View shown is the membrane binding B face of pCRP, with phosphocholine (cream spheres) and Ca2+ ions (black spheres) located in the ligand binding site on each subunit. The exposed region of the CHO-binding motif (residues 35–47) is coloured white in each subunit. The cross-sectional size of the pentamer is ∼100 Å (∼10 nm). (b) Close-up view of a phosphocholine head group from a microvesicle LPC molecule (light grey, orange, red, blue and white sticks) bound in the ligand binding site of one pCRP subunit (cream cartoon). Some of the residues lining the ligand binding site are labelled (using one letter amino-acid codes) and shown as sticks, the two Ca2+ ions are green spheres. Salt bridge interactions between the phosphocholine amine group and Glu81 (E81) are indicated by black dashed lines. (c) Interaction of pCRP with a model CHO:POPC bilayer (CHO shown as cream coloured sticks; POPC as light grey, orange, red, blue and white sticks). The ligand binding site on each pCRP subunit can bind to a phosphocholine head group of POPC as shown in (b) for an LPC molecule. View is from above, looking down onto the pCRP A face and showing the pentameric conformation. The diameter of the pentamer inner annular void is ∼30 Å (∼3 nm). (d) Side view showing the interaction between the B face of pCRP and the POPC phosphocholine head groups in the bilayer. The conversion of pCRP to pCRP* is a reversible process. (e) pCRP* in a pentameric conformation, same view as in (c). As the individual CRP subunits move apart, the neoepitope (residues 199–206, coloured yellow) is exposed and available for anti-mCRP-specific antibody (9C9 or 3H12) binding. The cross-sectional size of the pCRP* pentamer is ∼108 Å (∼10.8 nm). (f) The cross-section size of the complement C1q globular head group (PDB ID: 1PK6; ref. 47) is ∼50 Å (∼5 nm), this is the C1q domain that interacts with pCRP*. (g) and (h) The globular head of C1q inserts itself into the inner annular void of pCRP* forcing the subunits further apart. The interacting residues lie on the inner annular surface of the pCRP* pentamer and on the C-terminal surface of the C1q globular head group. The globular head group of C1q is physically unable to bind to pCRP. In (h) only one collagen-like fibre is shown (labelled as C1q collagen-like stem). We used part of a free art image for the coiled spring in (h) from www.vecteezy.com.