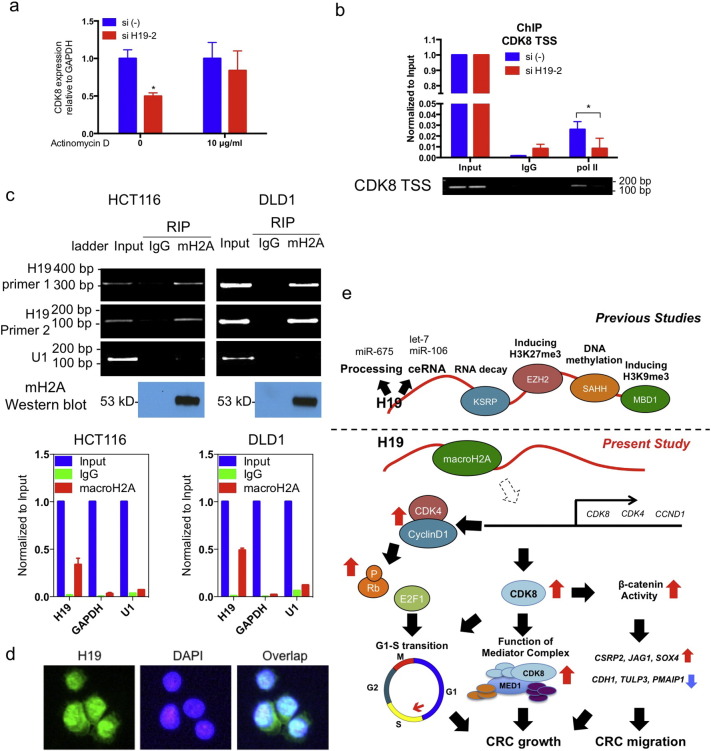
Fig. 6.
Mechanistic link between H19 and CDK8 expression. (a)CDK8 expression after exposure to siH19 for 12 h as determined by qRT-PCR in presence or absence of actinomycin D. (b)H19 silencing reduces polymerase II binding of transcription start site of CDK8 by chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments. (c)H19 interacts with macroH2A protein, by RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP). (d) In situ hybridization shows H19 expression in both nucleus and cytosol of HCT116 cells. (e) A scheme of H19 action: we provided additional insights of H19 on Rb-E2F1 signaling and CDK-β-catenin activity. We propose that H19 interacts with macroH2A, and this may consequently lead to de-repression of genes including CDK8, CDK4, and CCND1. Increased CDK4-cyclin D1 complex phosphorylates Rb to disrupt Rb-E2F1 interaction, leading to E2F1 activation. The increase of CDK8 expression enhances the function of mediator complex including MED1, and facilitates the gene regulation by β-catenin. These downstream targets could work in a synergistic way of promoting cell proliferation and increasing cell motility in CRC. See also Fig. S6.