Fig. 1.
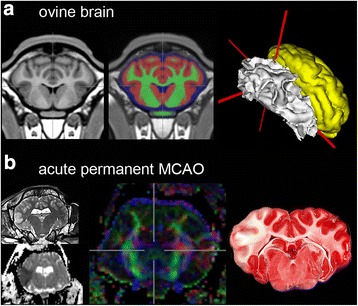
Focal ischaemic lesions in ovine brain. a Adult sheep brain in coronal section. T1-weighted population-averaged brain template (left), depiction of grey and white matter, as well as cerebrospinal fluid (middle panel, overlay on template) and surface reconstruction of white (white) and grey matter (yellow) in stereotactic space (right). Grey and white matter spaces are derived from a priori tissue probability maps. b Focal ischaemic lesion, 6 h after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO). Hyperintense area is seen in the left temporal cortex and medulla in T2-weighted TSE MRI (left-top). In this area, a decreased diffusion in apparent diffusion coefficient maps of diffusion weighted imaging (DWI-ADC, left-bottom) is visible. Fractional anisotropy map of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI-FA, middle panel) reveals a loss of fibre integrity. Following sacrifice and brain removal, the mitochondrial marker TTC labels living cells (red). The ischaemic lesion is unlabelled by TTC (right)
