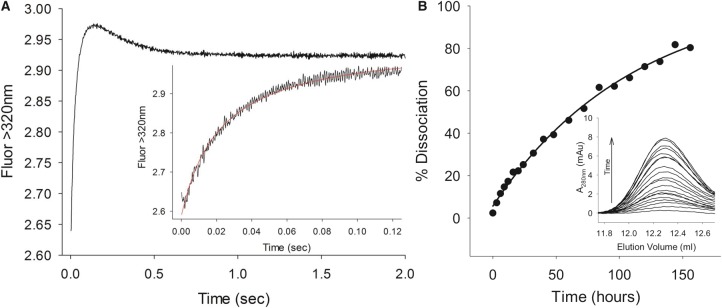
Figure 1. Measurement of ColE9–Im9 association and dissociation kinetics.
(A) Association kinetics of Y324C, L447C ColE9–Im9 complex monitored through tryptophan fluorescence (λex = 280 nm and λem > 320 nm) under second-order conditions in PBS, pH 7.4. Equimolar concentrations of the two proteins (0.7 µM before mixing) were mixed at 25 °C; the initial fluorescence enhancement and subsequent quench in fluorescence were fitted to second-order and first-order rate equations, respectively. Complex formation between Y324C, L447C ColE9 and Im9 is characterized by a bimolecular collision with a rate constant (k1) of 1.13 ± 0.06 × 108 M−1 s−1, followed by a conformational change with an apparent rate constant (k2 app) of 2.49 ± 0.02 s−1 (values derived from three independent measurements). These values are comparable to those we observed for wild-type ColE9 under the same conditions (k1 = 1.28 ± 0.03 × 108 M−1 s−1 and k2 app = 2.76 ± 0.02 s−1; data not shown) and very similar to those reported previously [22]. (B) Dissociation of Im9 from the Y324C, L447C ColE9–Im9 complex monitored through the accumulation of E9 DNase–Im9 complex as a function of time. Inset: Quantification of E9 DNase–Im9 complex through size-exclusion chromatography on a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column. The dissociation rate constant of 2.5 ± 0.2 × 10−6 s−1 determined here, in duplicate for Y324C, L447C ColE9–Im9 in PBS, pH 7.4, is in good agreement with that determined previously for wild-type ColE9 (2.1 × 10−6 s−1 in 50 mM Mops, pH 7.0, 200 mM NaCl) [22].