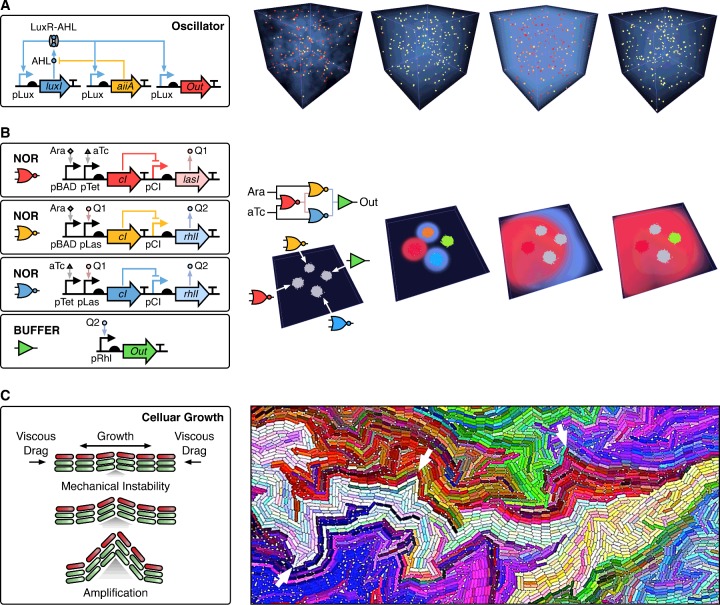
Figure 2. Agent-based models in synthetic biology.
Boxes contain the physical rules or genetic circuit controlling the behaviour of each cell. Multicellular agent-based simulations are shown to the right illustrating the emergent behaviours that arise. (A) Robust synchronized oscillations across a population of cells [27]. Each cell encodes an identical genetic circuit able to generate oscillations in the expression of an output gene (Out). The luxI gene encodes an enzyme that catalyses the production of N-acylhomoserine lactone (AHL). AHL binds to the constitutively produced LuxR protein (not shown), which activates the pLux promoters. AHL can also diffuse through the cell membrane into the environment to affect other cells (shown by the blue semi-transparent fog), and is negatively regulated by the aiiA gene whose product degrades AHL. The simulation shows 200 cells (small spheres) that start with random initial expression levels of circuit genes in a 100 μm3 box with wrapping boundary conditions. The colour of each cell corresponds to the expression of the output (yellow=low; red=high) (B) Four spatially separated colonies that collectively implement an EQUAL logic function (output is active when both inputs are simultaneously inactive or active) by using diffusing quorum molecules as chemical wires for communication [36]. The genetic circuit for each colony is shown that implements either a NOR or BUFFER logic function. Arabinose (Ara) and anhydrotetracycline (aTc) are used as inputs to the circuit. Q1 and Q2 are the quorum-sensing molecules 3OC12-HSL and C4-HSL respectively. These are able to diffuse through the cell membrane into the environment and are shown by the red (Q1) and blue (Q2) semi-transparent fogs that propagate in the simulations. Each colony in the simulation consists of 20000 cells, which are coloured if the output promoter (pCI) is active. The simulation starts with all cells inactive and both arabinose and aTc absent from the medium. (C) Generation of fractal colony structures through accurate agent-based modelling of rod-shaped bacteria colony growth. The simulation image is adapted from http:://cellmodeller.org and shows cells coloured according to their mother–daughter relationship. On division, the daughter cell colour is chosen on the basis of its mother colour with a small random change. Several points of mechanical instability are highlighted with white arrows. Simulations in (A) and (B) were generated using BSim [39] and (C) using CellDesigner [63]. Genetic circuits are shown using Synthetic Biology Open Language Visual (SBOLv) notation [84] and generated using DNAplotlib [85].