Fig. 15.
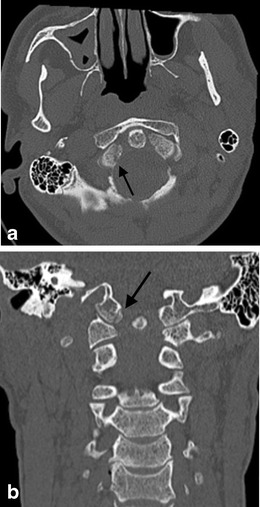
Type III occipital condyle fracture: a axial CT image through the atlanto-occipital level performed as part of a polytrauma CT assessment of a young female pedestrian struck by a motorcyclist travelling at speed; b coronal CT image of the same patient. The type III occipital condyle fracture can be subtle on CT imaging [indicated here on the right (arrow)] but may indicate a high-energy traumatic mechanism to the craniocervical junction with potentially unstable craniocervical spine injury related to alar ligament avulsion
