Figure 2.
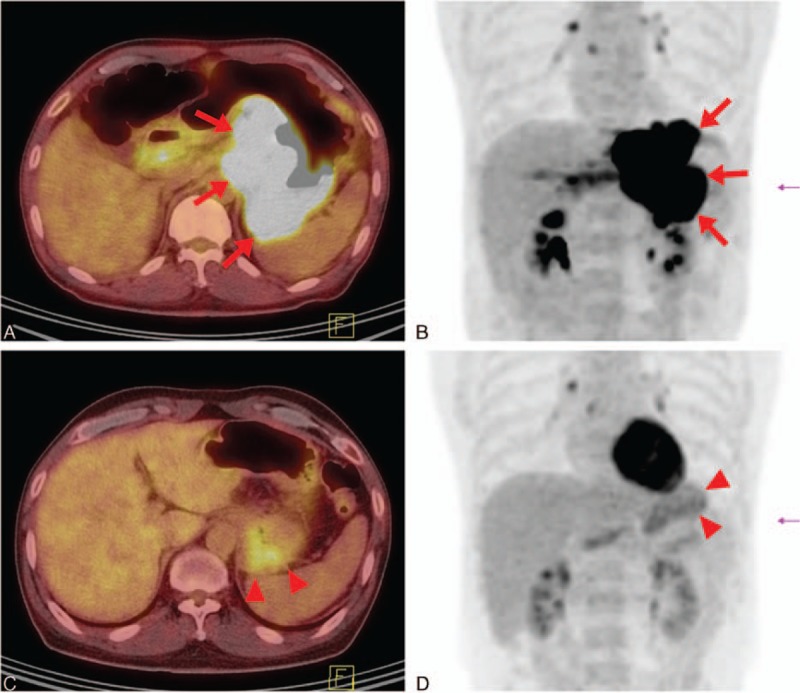
A 53-year-old man with gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. In baseline positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) transaxial (A) and PET maximum intensity projection (MIP) (B) images, intense F-18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose (FDG) uptake was seen along the gastric wall from cardia to body, mainly along the lesser curvature side (maximum standardized uptake value 28.2) (arrows). In interim PET/CT transaxial (C) and PET MIP (D) images after 3 cycles of first-line chemotherapy, previously noted FDG uptake in the stomach showed markedly decreased intensity and extent (arrowheads). Remaining FDG uptake could not be differentiated from physiological gastric activity. Reader A interpreted this finding as Deauville score 4 and reader B interpreted it as score 1. After completion of first-line chemotherapy, the patient remains in clinical remission without additional therapy (overall survival 76.8 months). CT = computed tomography, FDG = F-18-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose, MIP = maximum intensity projection, PET = positron emission tomography.
