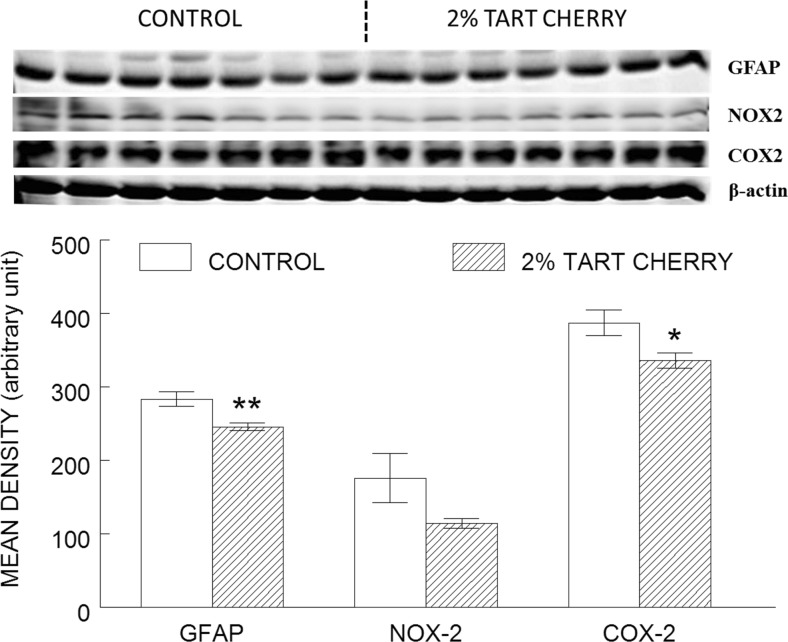
Fig. 4.
Tart cherry consumption reduced inflammation in the hippocampus. The results shown represent western blot (top) of inflammatory markers (glial fibrillary acidic protein [GFAP], NADPH oxidase-2 [NOX-2], and cyclooxygenase-2 [COX-2]) in the hippocampus of control (opened bar) and 2 % tart cherry-supplemented group (hatched bar), and densitometry analysis (bottom) of the immunoreactive bands normalized to β-actin, with results represented as mean ± SEM; n = 7/group. Asterisk indicates statistically significant difference between the groups (p < 0.05). Double asterisk indicates significant difference between the groups (p < 0.01)