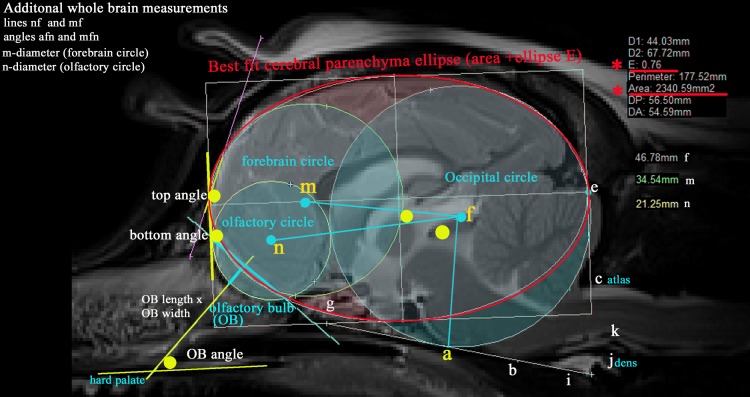
Fig 2. Additional morphometric measurements taken of the T2w mid-sagittal brain MRI of a CKCS with CM pain.
Key For identity of points a-l see Fig 1. Three ‘best fit’ circles (coloured aqua) and an ellipse (coloured red) that follow the outline shape of the neural parenchyma as closely as possible. Occipital circle (centre f)–as for hindbrain study. Size is determined by the shape of the occipital lobe extending rostroventrally to the baseline labi (basioccipital bone). i Forebrain circle (centre m)—most rostral portion of the forebrain dorsal to the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone. ii Olfactory circle (centre n)—size is determined by the shape of olfactory bulbs extending beyond the pre-frontal cortex in the mid-sagittal image. iii Cerebral parenchyma ellipse which encompasses the caudal edge of the occipital and rostral edge of the forebrain circle (i.e. the cerebral parenchyma but not including the entire cerebellum or brainstem), its area (mm2) together with its ellipticity ‘E’ (defined as a mathematical relationship between of the largest radius to the smallest radius in the ellipse). Both calculated by Mimics Materialise® software programme. (smaller E values = more spherical, larger E values more elliptical). iv Associated lines (coloured aqua) comprising mf, nf, The olfactory bulb (OB) length and height (product represented. v Five angles (coloured yellow): • top angle—angulation between the frontal and parietal lobes. • bottom angle -angulation between the dorsal OB and the frontal lobe. • OB angle—angulation between the OB and hard palate. • mfn and nfg.