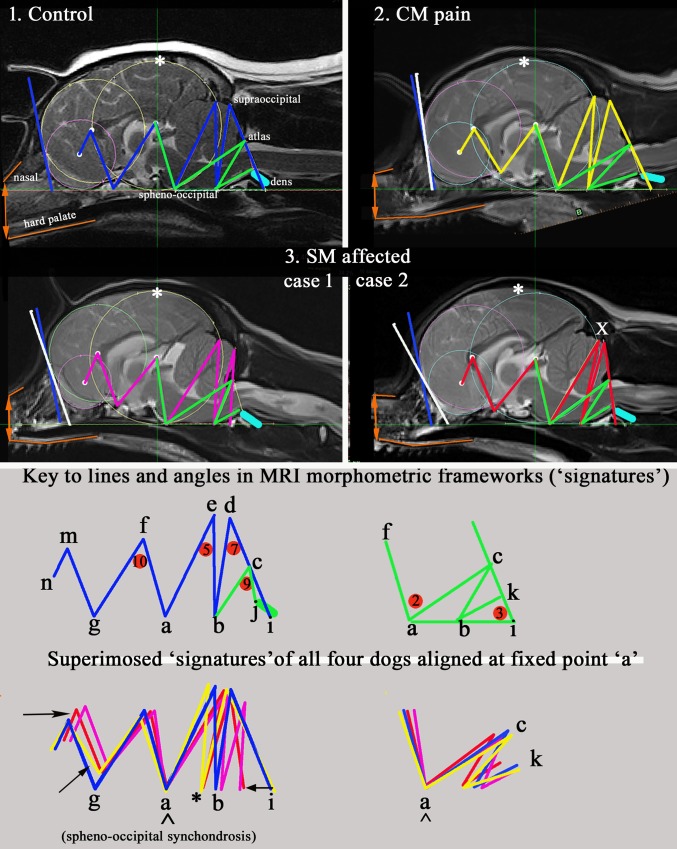
Fig 5. Four mid-sagittal T2w whole brain MRI exemplars of cohorts Control, CM pain and two conformation cases of SM.
The occipital circle has been standardised in all the images and the baseline labi aligned to facilitate comparison. Colour codes for morphometric ‘signatures’: Blue = Control; Yellow = CM pain; Red/Crimson = SM affected (two cases). Green: all groups = angles 2 and 3 and lines bc and bk. Superimposed- CM pain (yellow) has most extreme range. White: *greatest parenchyma height from skull baseline and is rostral to occipital circle in CM pain and SM affected case 2. x caudal displacement of occipital lobe. white/blue bar drawn at most rostral point of forebrain and olfactory circles indicates angulation of forebrain flattening. The blue bar (Control dog) has been superimposed on the three other group dogs for comparison. CM pain has greatest rostral forebrain flattening; The SM case 2 has the greatest olfactory lobe deviation.Orange: brachycephaly- lines mark the position and relationship of the upper nasal bone and the hard palate. SM case 2 has the greatest brachycephaly with angulation at the nasion and the lower palatine/incisive bones. Aqua: dens. This lies closest to the basioccipital in SM case 1. The different angle of dens in CM pain dog was found to be significant for the study. Black: arrows suggest displacement resulting from craniosynostosis. * indicates deviation (shortening) of occipital bone in CM pain and SM case 2.