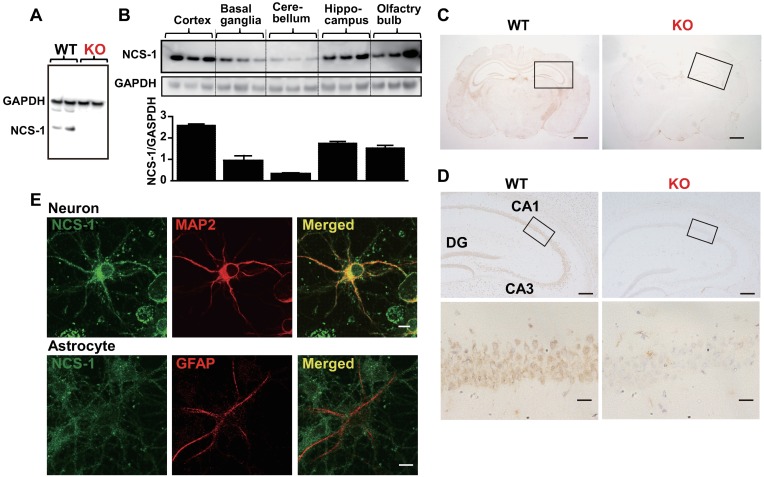
Fig 2. Localization of neuronal calcium sensor-1 (NCS-1) in the mouse brain.
(A and B) Western blotting of brains from wild-type (WT) and Ncs1-/- (knock-out [KO]) mice was performed with anti-NCS-1 monoclonal antibody to evaluate the specificity of antibody (A) and examine the localization of NCS-1 in different regions of brain (B). Anti-GAPDH antibody was used for normalization. (C) Cross-sections of the brains of 6-week-old WT and KO mice subjected to immunohistochemistry for NCS-1. The nuclei were counterstained with hematoxylin and visualized in blue. Scale bars = 1 mm. (D) Higher magnification images of the hippocampus in C. CA1: Cornu Ammonis 1; CA3: Cornu Ammonis 3; DG: dentate gyrus. Scale bars = 200 μm (upper panels) and 20 μm (lower panels), respectively. (E) Representative images of immunocytochemistry showing a MAP2-positive cortical neuron (red signals in upper panels) and a GFAP-positive astrocyte (red signals in lower panels), labeled with NCS-1 (green signals in upper and lower panels), isolated from the cortex of a WT mouse embryo (E18). Scale bar = 10 μm. MAP2: Microtubule-associated protein 2; GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.