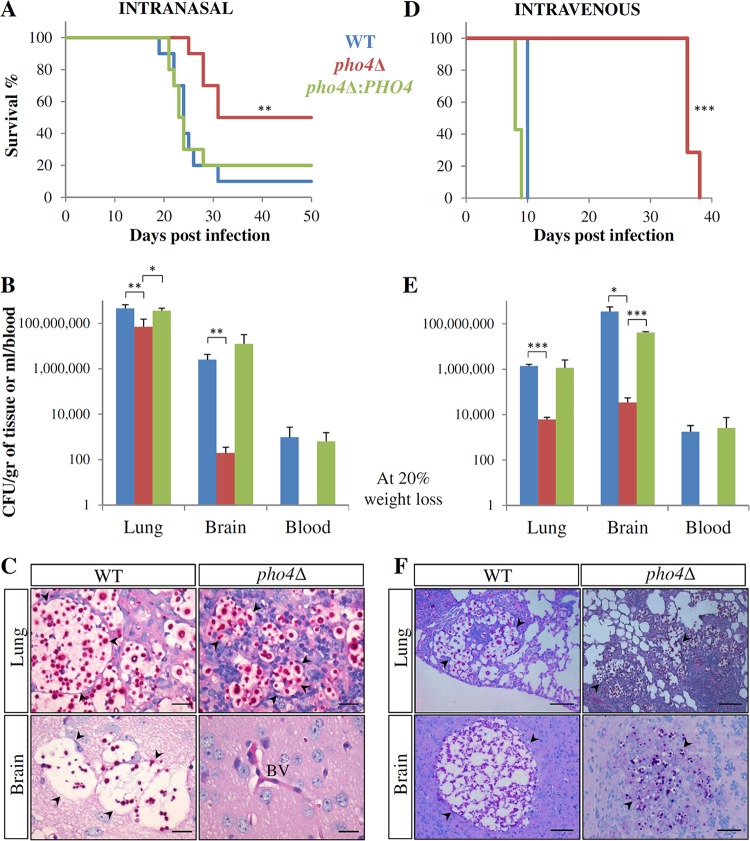
FIG 3 .
The pho4Δ mutant is less virulent than the WT strain in intranasal (A to C) and intravenous (D to F) models of cryptococcosis. (A) Survival of C57BL/6 mice infected intranasally with 5 × 104 WT, pho4Δ+PHO4, or pho4Δ cells (10 mice in each group). Mice infected with the pho4Δ mutant survived longer than mice infected with the WT strain (**, P = 0.002). (B) Mean CFU from the lungs, brains, and blood from five mice that had succumbed to infection in each group. Compared to mice infected with the WT strain and the pho4Δ+PHO4 strain, which had similar numbers of lung CFU (P = 0.6288), the number of lung CFU of mice infected with the pho4Δ mutant was lower than the numbers for mice infected with the WT and pho4Δ+PHO4 strains (**, P = 0.0094; *, P = 0.0496). The numbers of brain CFU were similar for WT-strain- and pho4Δ+PHO4 strain-infected mice (P = 0.4756) but lower for pho4Δ mutant-infected mice (**, P = 0.0039). No CFU were obtained from the blood of mice infected with the pho4Δ mutant. (C) PAS-stained histological sections of lung and brain samples collected from mice infected with the WT strain and the pho4Δ mutant at the time of illness. (D) Survival of mice infected intravenously with 5 × 103 WT, pho4Δ+PHO4, and pho4Δ yeast cells. The difference in survival between WT-strain- and pho4Δ+PHO4 strain-infected mice and pho4Δ mutant-infected mice was 25 days (***, P < 0.0001). (E) pho4Δ CFU were significantly lower in the dissemination model in both the lung (***, P < 0.0001) and brain (*, P = 0.0195; ***, P < 0.0001). (F) PAS-stained sections of lung and brain samples at the time of illness revealed reduced dissemination of pho4Δ cells to both the lung and brain compared to WT and pho4Δ+PHO4 cells. Some cryptococcomas are indicated by black arrowheads. BV, blood vessel. Bars, 100 µm.