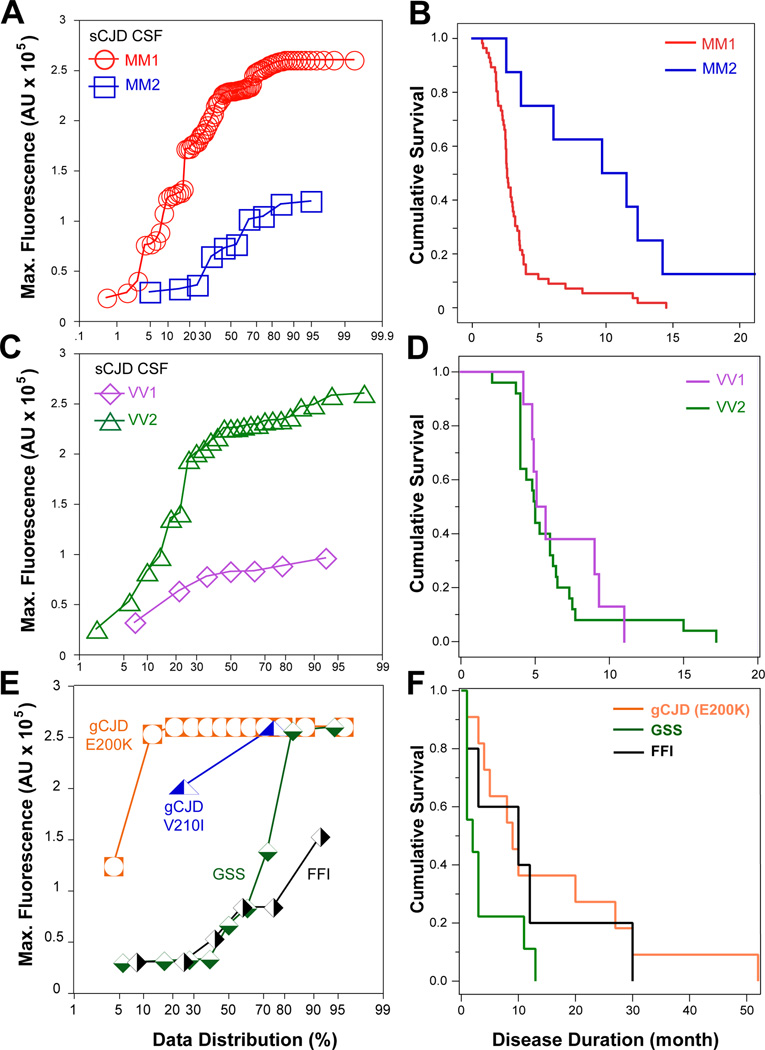
Figure 3.
Differentiation of major human prion subtypes based on seeding potency in second-generation CSF RT-QuIC and relationship with the disease progression rate. (A) Individual data distribution of maximum CSF second-generation RT-QuIC fluorescence obtained in sCJD MM1 (n = 90) and sCJD MM2 (n = 10). (B) Cumulative survival curves of sCJD cases plotted in Figure 3A. (C) Cumulative plot of CSF RT-QuIC data obtained in sCJD VV1 (n = 7; outlier with no remaining CSF for retesting is not plotted) and in sCJD VV2 (n = 25). (D) Cumulative survival curves of sCJD cases plotted in Figure 3C (E) Cumulative plot of CSF RT-QuIC data obtained in genetic prion disease (E200K, n = 12; V210I, n = 2), GSS (n = 9), and FFI (n = 6) (F) Cumulative survival curves of the genetic prion cases plotted in Figure 3E.