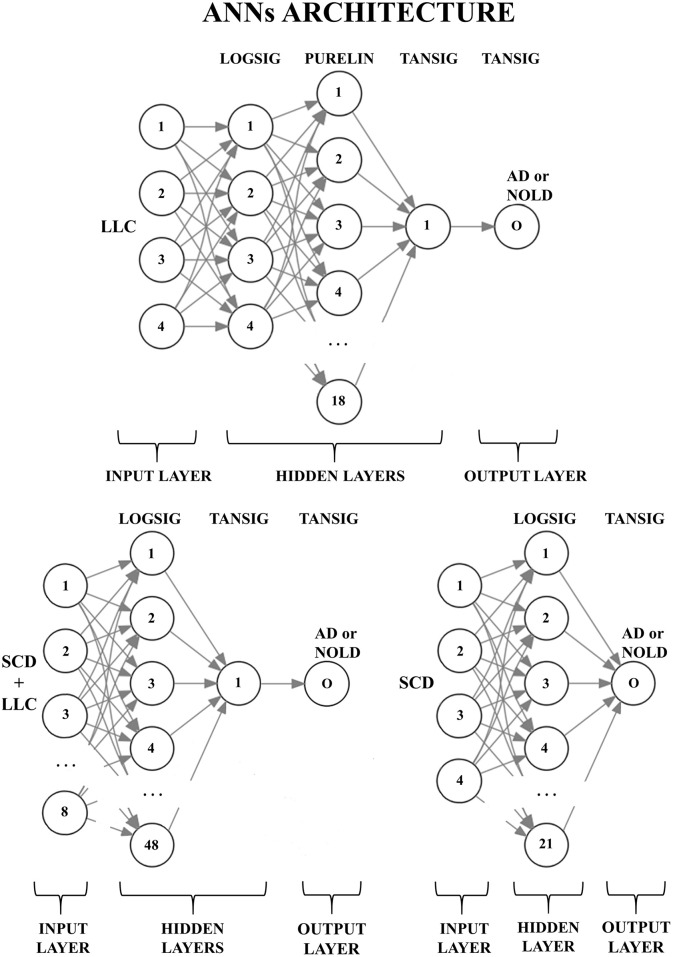
Figure 2.
Structures of the three artificial neural networks (ANNs) used to classify Alzheimer's disease patients with dementia (AD) from Normal elderly subjects (Nold). EEG markers are given as inputs in the first layer (input layer); every node (the numbered circles) of every successive layer (i.e., the hidden layers and the output layer) is characterized by an activation function: A non-linear function to decide, in analogy with biological neurons, the output of the node (0 or 1). The output node (O) provides the classification result (AD or Nold). Legend for the input markers: (top) the four best Lagged Linear Connectivity (LLC) markers; (bottom left) the four best LLC markers together with the four best Source Current Density (SCD) markers; (bottom right) the four best SCD markers. Legend for the activation functions: log-sigmoid (logsig), linear (purelin), and tan-sigmoid (tansig).