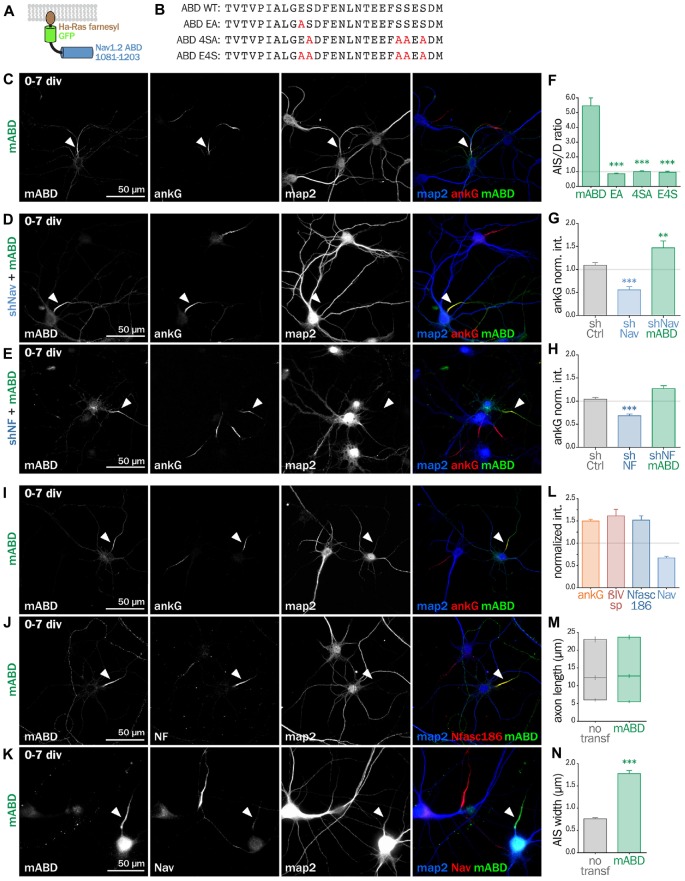
Figure 6.
Synthetic mABD construct rescues Nav or Nfasc186 knockdown and upregulates AIS formation. (A) Schematic representation of the mABD construct composed of the amino-acids 1081–1203 of rat Nav1.2 fused to a GFP with a farnesylation motif from Ha-Ras in its C-terminal. (B) Alignment of wild type (WT) and mutated sequences corresponding to the rat Nav1.2 (aa 1102–1128) Ankyrin Binding Domain (ABD). The mutated amino-acids involved in ankG binding are in red. Rat hippocampal neurons transfected at 0 div with mABD alone (C,I,J,K) or in association with shNav (D) or shNF (E), fixed 7 days later (div 7), and immunostained for GFP, map2 and ankG (C–E,I), Nfasc186 (J) or Nav (K). Arrowheads indicate the AIS of transfected neurons. (F) Ratio of the mean fluorescence intensity for GFP labeling in the proximal axon compared to the mean of three dendrites (D) in each transfected neuron (mABD 5.46 ± 0.54, n = 77, mABD-EA 0.86 ± 0.06, n = 37, mABD-4SA 1.01 ± 0.05, n = 36; mABD-E4S 0.96 ± 0.07, n = 32; two independent experiments). (G,H) Ratio of the mean fluorescence intensity for ankG labeling at the AIS of transfected neurons compared to surrounding untransfected neurons (G: shCtrl 1.09 ± 0.06, n = 54; shNav 0.56 ± 0.07, n = 21; shNav + mABD 1.47 ± 0.15, n = 23; two independent experiments. H: shCtrl 1.04 ± 0.04, n = 61; shNF 0.68 ± 0.04; n = 64; shNF + mABD 1.27 ± 0.07, n = 49; two independent experiments). (L) Ratio of the mean fluorescence intensity for ankG, ßIV-spectrin (ßIVsp), Nfasc186 or Nav labeling at the AIS of transfected neurons compared to surroundings untransfected neurons (ankG 1.50 ± 0.04, n = 146; ßIVsp 1, 52 ± 0.10, n = 49; NF 1, 62 ± 0.14, n = 26; Nav0.67 ± 0.04; n = 33; 2–6 independent experiments). (M,N) Length and width of the AIS in mABD-transfected neurons (untransfected cells AIS width 0.76 ± 0.03 μm, n = 61; mABD 1.78 ± 0.07 μm, n = 60; two independent experiments).