Fig. 2.
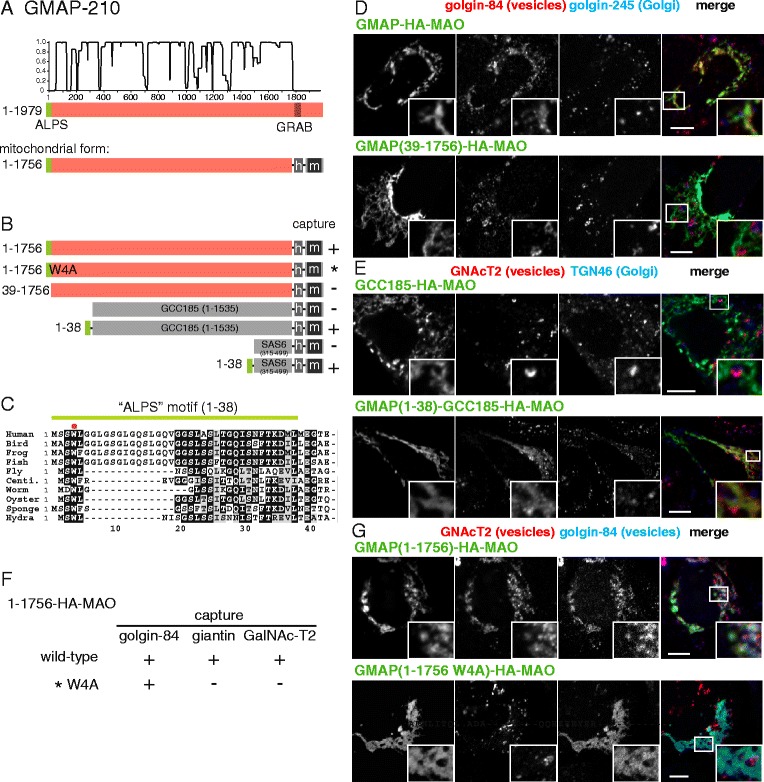
Mapping the vesicle capturing activities of GMAP-210. a Schematic diagram of human GMAP-210 with plots for the predicted degree of coiled-coil and disorder. In the mitochondrial form, the Golgi-targeting transmembrane domain (TMD) is replaced with a hemagglutinin (HA) tag (h) and the TMD of human monoamine oxidase A (m). b Summary of the vesicle capture activity of the indicated variants of mitochondrial GMAP-210. Capture at mitochondria was assayed by immunofluorescent staining of the Golgi integral membrane proteins golgin-84, giantin and GalNAc-T2. Plus sign indicates that capture of all three markers was similar to the wild-type protein, minus sign indicates that no significant capture was observed. c Alignment of the N-terminus of human GMAP-210 with that from the indicated species. Bird, G. gallus; fish D. rerio; frog, X. tropicalis; urchin, S. purpuratus; fly, D. melanogaster; centipede, S. maritima; worm, S. mansoni; oyster, C. gigas; sponge, A. queenslandica; hydra, H. vulgaris. Well conserved residues are shaded, and indicated as a green bar is the amphipathic lipid-packing sensor motif reported previously for the human protein [17], and by a red dot the conserved tryptophan mutated in this study. d, e Confocal micrographs of HeLa cells expressing the indicated GMAP-210 variants and stained for the HA tag on the chimera as well as for the indicated proteins in vesicles captured by GMAP-210, or for Golgi proteins that are not captured. Cells were treated with nocodazole for 6 h prior to fixation to ensure that mitochondria were close to intra-Golgi transport vesicles. Key constructs from the set shown in (b) are included, with similar results obtained using the marker giantin. Scale bars 10 μm. f, g As in (d and e), except comparing the complete GMAP-210 coiled-coil region with a variant in which Trp4 is mutated to alanine. This results in loss of tethering of some vesicle cargo but not golgin-84. Scale bars 10 μm
