Fig. 2.
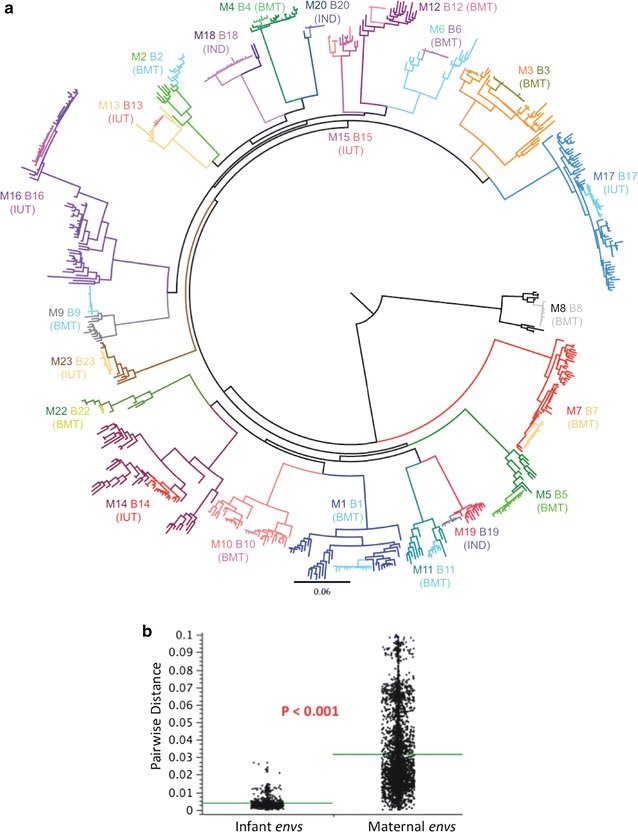
Genetic analysis of HIV envelope sequences among MTCT pairs. a Phylogenetic tree of all 22 mother–infant transmission pairs included in study. All maternal envelopes form distinct phylogenetic clusters, with infant envelopes forming a subcluster within the larger maternal cluster. Infant envelopes are colored differently from the maternal envelopes (often in a lighter shade). b Comparison of infant versus maternal envelope diversity was performed using the approach described by Gilbert et al. [104] for comparing genetic distances. Infant envelopes (shown on the left) were significantly less diverse than maternal envelopes (p < 0.001)
