Figure 6.
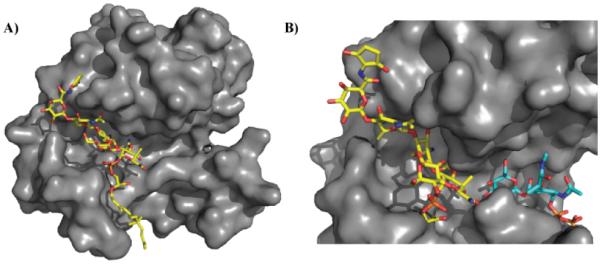
Site of moenomycin interaction with glycosyltransferases. A) Crystal structure of moenomycin (yellow) bound to S. aureus monofunctional transglycosylase (PDB 3HZS). Only 15 carbons of the lipid tail are ordered in this structure. B) Crystal structures of membrane-bound monofunctional glycosyltransferase with moenomycin (yellow; PDB 3VMR) and a lipid II analog (blue; PDB 3VMT). Note: 3VMR and 3VMT were aligned, and the surface of 3VMR was subsequently hidden for clarity. Moenomycin binds in the channel where the growing glycan chain binds thereby disrupting transglycosylation activity. Under normal biological conditions, lipid II would be transferred to the growing glycan chain forming a new β1-4 glycosidic linkage.
