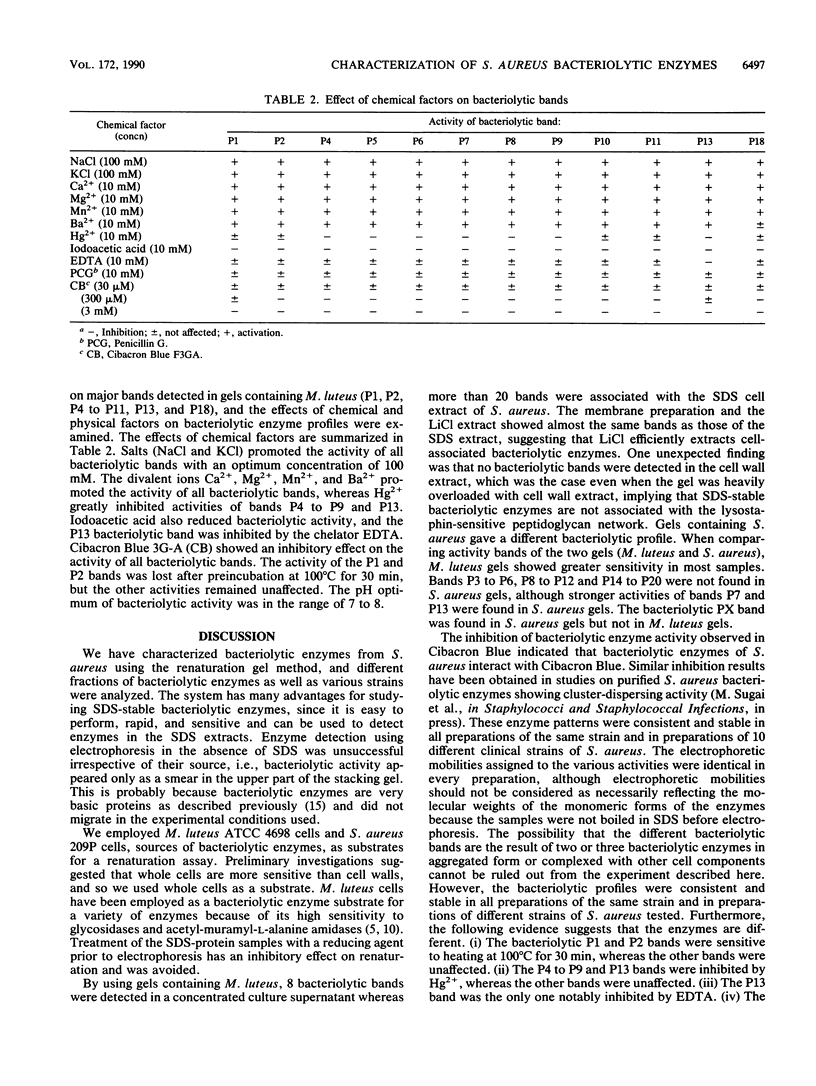
Abstract
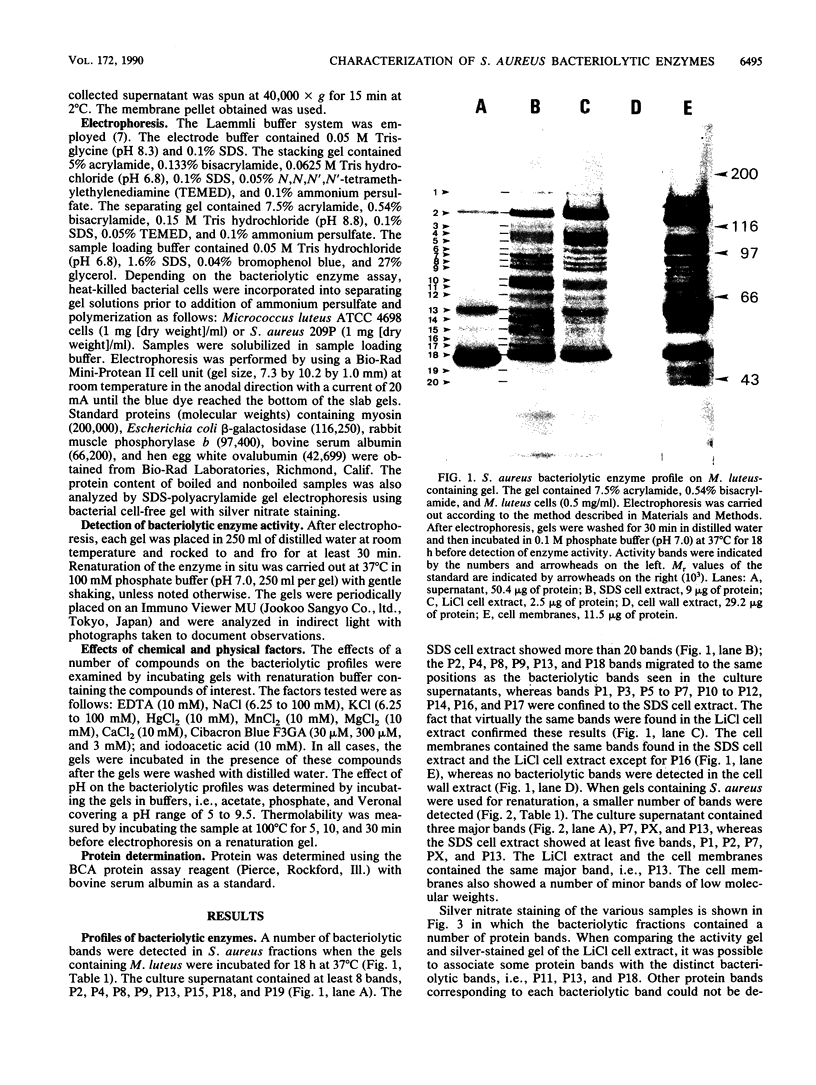
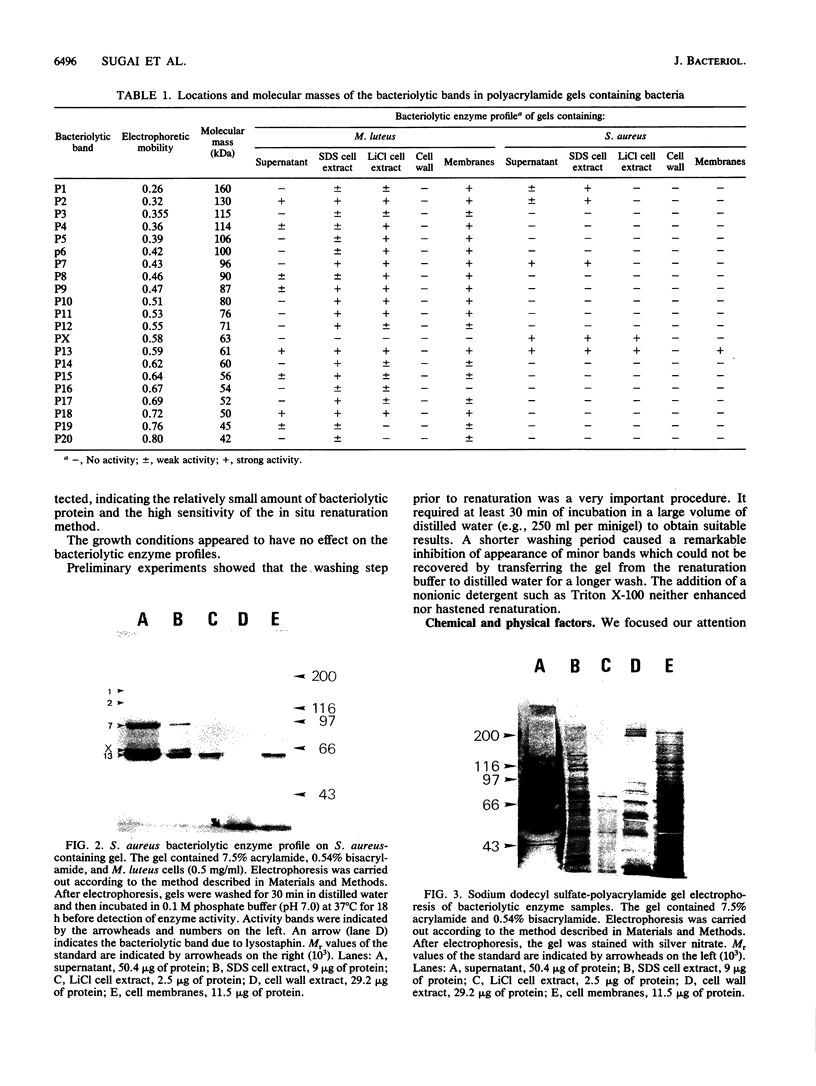
Profiles of the bacteriolytic activities of Staphylococcus aureus culture supernatants, sodium dodecyl sulfate cell extracts, LiCl cell extracts, cell wall extracts, and cell membranes were analyzed in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels containing Micrococcus luteus or S. aureus. A total of 20 distinct bands of bacteriolytic activity could be detected in gels containing M. luteus, 8 of these bands were found in culture supernatants. The sodium dodecyl sulfate cell extracts, the LiCl cell extracts, and the cell membranes each contained 20 bands (P1 to P20), but no activity was found in cell wall extracts. Less bacteriolytic activity could be detected in gels containing S. aureus, although three bands were found in culture supernatants and LiCl extracts and cell membranes contained one major band, P13. Crude cell extracts showed five bacteriolytic bands of which the major bacteriolytic bands were distributed in an identical manner in all 10 strains of S. aureus studied. The effects of chemical and physical factors were determined, and it was shown that iodoacetic acid, Hg2+, and Cibacron Blue 3G-A reduced activity, and an optimum pH for enzyme detection was between 7 and 8. Preincubation at 100 degrees C for 30 min reduced the activity of P1 and P2 bands.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audy P., Grenier J., Asselin A. Lysozyme activity in animal extracts after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1989;92(3):523–527. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(89)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. L., Fischetti V. A. Variation in the expression of cell wall proteins of Staphylococcus aureus grown on solid and liquid media. Infect Immun. 1988 May;56(5):1061–1065. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.5.1061-1065.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubak B. M., Yotis W. W. Staphylococcus aureus adenosine triphosphatase: inhibitor sensitivity and release from membrane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):385–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.385-390.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc D., Asselin A. Detection of bacterial cell wall hydrolases after denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Aug;35(8):749–753. doi: 10.1139/m89-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro A. L., Viñuela E., Maizel J. V., Jr Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Sep 7;28(5):815–820. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90391-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheagren J. N. Staphylococcus aureus. The persistent pathogen (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 May 24;310(21):1368–1373. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405243102107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheagren J. N. Staphylococcus aureus. The persistent pathogen (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1984 May 31;310(22):1437–1442. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405313102206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugai M., Koike H., Hong Y. M., Miyake Y., Nogami R., Suginaka H. Purification of a 51 kDa endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 Oct 15;52(3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadström T. Bacteriolytic enzymes from Staphylococcus aureus. Properties of the endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. Biochem J. 1970 Dec;120(4):745–752. doi: 10.1042/bj1200745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]