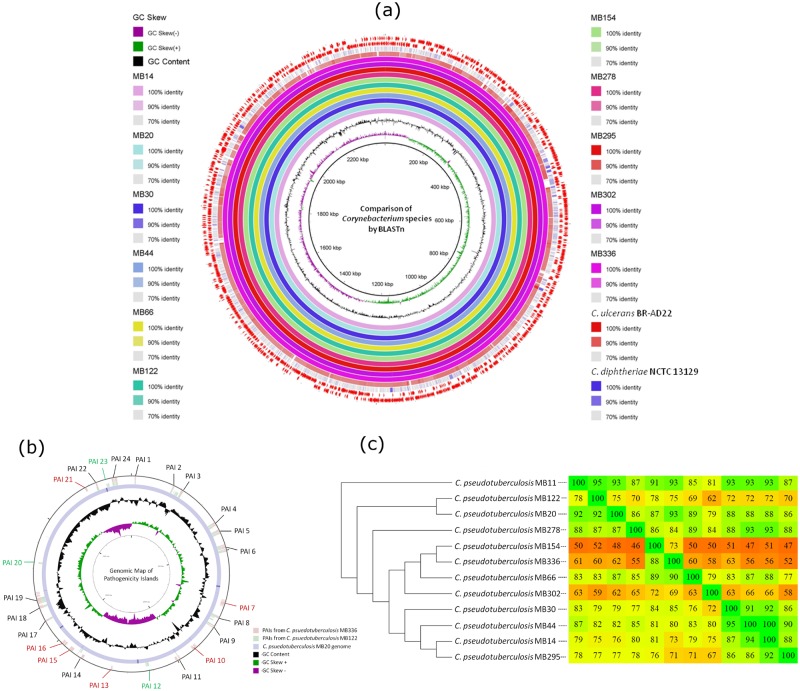
Fig 1. Map of the circular genomes of C. pseudotuberculosis, C. ulcerans and C. diphtheriae and the analysis of GEIs.
The genomes were compared by blastn, and the percentage of identity between them was determined by the intensity of the color in the circular map. The genomes of C. pseudotuberculosis were identified only by the name of the lineage. (a) The innermost ring to the outermost is presented in this figure, as follows: the GC skew of the MB14 strain; the GC contents of the MB14 strain, the genomes of the C. pseudotuberculosis strains MB14, MB20, MB30, MB44, MB66, MB122, MB154, MB278, MB295, MB302, and MB336, and the genomes of C. ulcerans BR-AD22 and C. diphtheriae NCTC 13129. The two outermost rings comprise CDSs identified in the genome of C. pseudotuberculosis MB14. The graph displayed by GC skew is common to chromosomes that have bidirectional replication. (b) A circular genome map of the MB20 strain was constructed by comparing the position of 18 PAIs in the MB122 strain and 21 PAIs the in MB336 strain through tblastx. The PAIs shown in black were detected in both strains by GIPSy, while the PAIs in green were detected only in MB122 and the PAIs in red were detected only in MB336. A later comparison using blastn showed that the conservation of these PAIs was higher than that observed by GIPSy. (c) A dendrogram was calculated with the Neighbor-Joining model from the comparison of the nucleotide sequences of the RIs of 12 Californian isolated genomes.