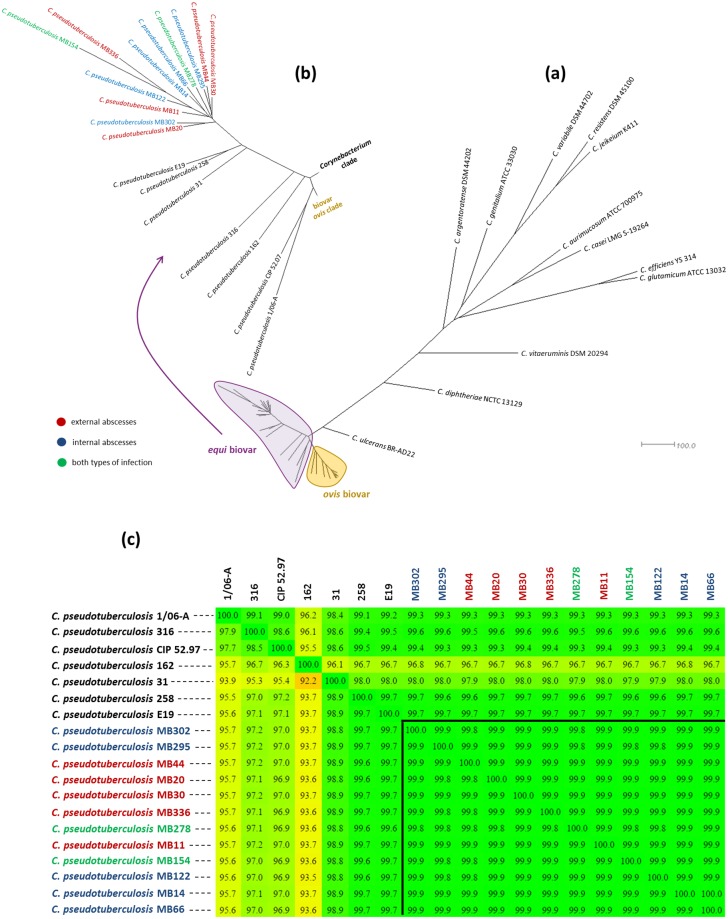
Fig 4. Phylogenomic analysis of the Corynebacterium genus.
(a) The entire Neighbor-Joining tree containing the Corynebacterium RefSeq genomes, demonstrating the closeness between the species C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans and C. pseudotuberculosis. This latter species comprises two distinct clades composed of strains from biovar ovis (marked in orange) and biovar equi (marked in purple). (b) An expanded view of the biovar equi tree. Strains isolated in California (in color) are closely related to each other. The strains CIP 52.97 and 1/06-A formed the outermost clade of biovar equi. The colors of the names from strains isolated in California distinguish the types of infection caused by the pathogen. (c) Dendrogram calculated with the Neighbor-Joining model from heatmap values generated in the Gegenees program. The values shown in the heatmap indicate the percentage of similarity between the analyzed genomes. The name of the species isolated in California is colored according to the type of infection caused by the pathogen.