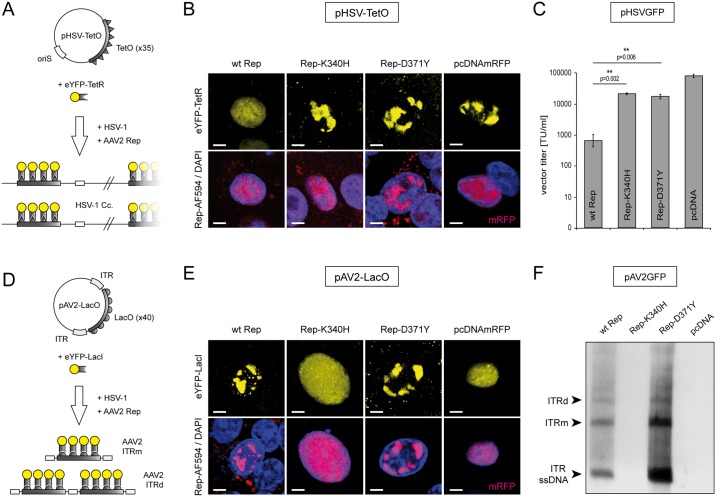
Fig 2. Effects of the different Rep constructs on HSV-1 and AAV2 DNA replication.
(A) Replication of an HSV-1 replicon is visualized with plasmid pHSV-TetO containing an HSV-1 origin of DNA replication (oriS) and a TetO-cassette consisting of 35x TetR binding sites. In presence of HSV-1 replication factors (HSV-1), the accumulation of pHSV-TetO replication products is visualized by binding of an eYFP-TetR fusion protein (yellow fluorescent RCs). (B) Cells expressing the different Rep constructs (indicated on top) were analyzed for the ability to inhibit HSV-1 replication. The presence of Rep proteins was confirmed by staining with a Rep-specific antibody (red; bottom panels). A cell transfected with pcDNAmRFP expressing the monomeric red fluorescent protein (mRFP) was used as a positive control. DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. Scale bar; 5μm. (C) Effects of the different Rep constructs on HSV-1 amplicon vector production. Vero 2–2 cells were transfected with the HSV-1 amplicon DNA (pHSVGFP), packaging-defective HSV-1 helper DNA (fHSVΔpacΔ27Δkn), HSV-1 ICP27 encoding plasmid (pEBHICP27) and the different Rep encoding plasmids. At 72 hrs post transfection the pHSVGFP amplicon vector particles were harvested and titrated on Vero cells. The data are shown as means ± standard errors (SE) from three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences based on a paired two-tail Student t-test (** = p<0.01). (D) Replication of an AAV2 replicon is visualized with plasmid pAV2-LacO, which is harboring a LacO-cassette consisting of 40x LacI binding sites flanked by AAV2 ITRs. In presence of the different Rep constructs and HSV-1 helper factors (HSV-1), the accumulation of pAV2-LacO replication products is visualized by binding of an eYFP-LacI fusion protein (yellow fluorescent RCs, top panels). (E) Cells expressing the different Rep constructs (indicated on top) were analyzed for the ability to replicate pAV2-LacO and accumulate corresponding RCs. A Rep-specific antibody was used to confirm the synthesis of Rep proteins in the transfected cells (red; bottom panels). A cell expressing mRFP was used as a negative control. DAPI was used to stain the nuclei. Scale bar; 5μm. (F) Vero 2–2 cells were transfected with pAV2GFP and the different Rep constructs as indicated. At 24 hrs after transfection, the cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI 2) and subjected to Hirt DNA extraction 48hrs later. Extrachromosomal DNA was digested with DpnI and analyzed by Southern blotting with a DIG-labeled probe specific for GFP. The ITR ssDNA, the monomeric (ITRm) and the dimeric (ITRd) AAV2 replication intermediates are indicated on the left.