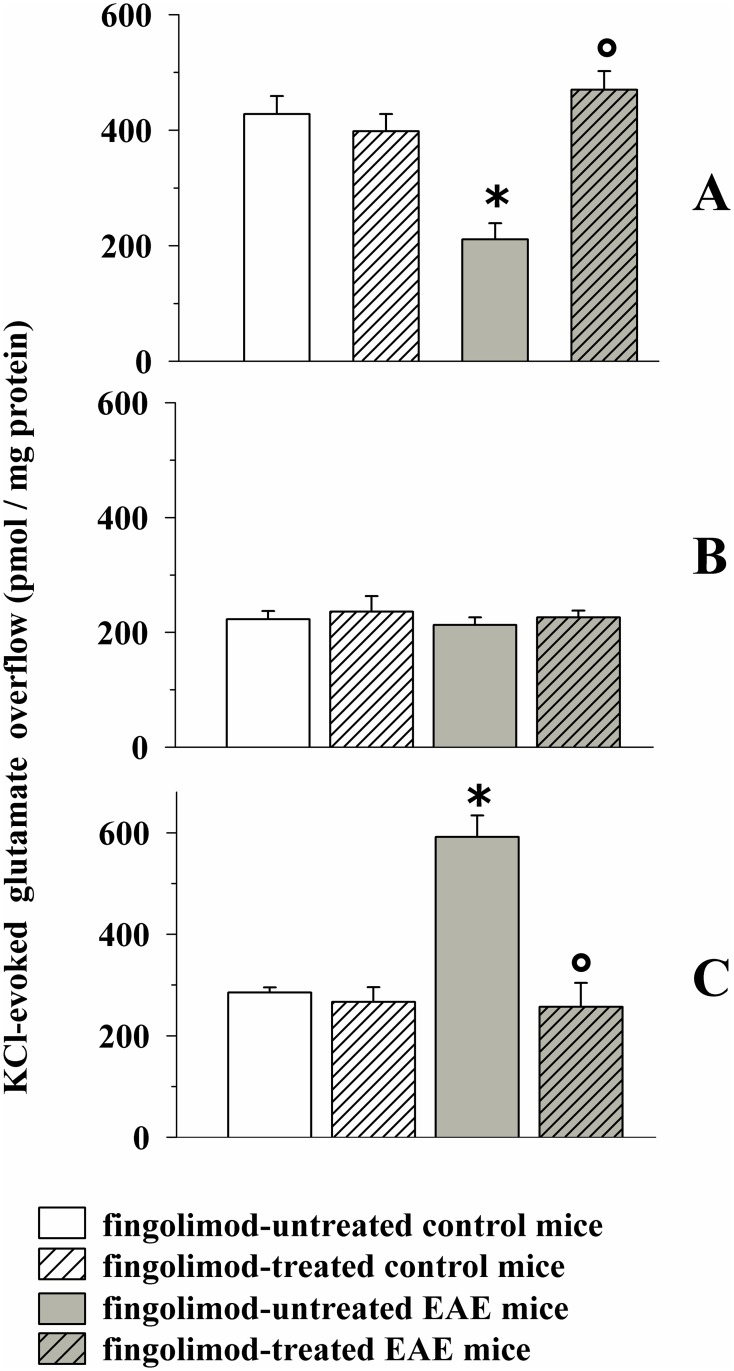
Fig 4. Effect of in vivo prophylactic fingolimod (0.3 mg/kg) on the depolarization-evoked exocytosis of endogenous glutamate from nerve terminals isolated from selected regions of the CNS of control and EAE mice.
Female mice were randomly assigned to the following groups: control mice (empty bar, n = 8 mice); fingolimod-treated control mice (rising-right hatched empty bar, n = 8 mice); EAE mice (grey bar, n = 8 mice); fingolimod-treated EAE mice (rising-right hatched grey bar, n = 8 mice). Fingolimod was administered in the drinking water for 14 days starting from 7 d.p.i. At 21 ± 1 d.p.i mice were sacrificed and cortical (A), hippocampal (B) and spinal cord (C) synaptosomes were isolated to monitor the exocytosis of endogenous glutamate elicited by a mild (12 mM KCl enriched superfusion medium for cortical and hippocampal synaptosomes and 15 mM KCl enriched superfusion medium for spinal cord synaptosomes) depolarizing stimulus. Results are expressed as KCl-evoked overflow; data are expressed as pmoles / mg protein and represent the mean ± SEM. Each experiment was carried out with the synaptosomal preparations isolated from one animal for each group, and it was run in triplicate (three superfusion chambers for each animal). * p < 0.05 at least versus control untreated mice; ° p < 0.05 at least versus EAE untreated mice.