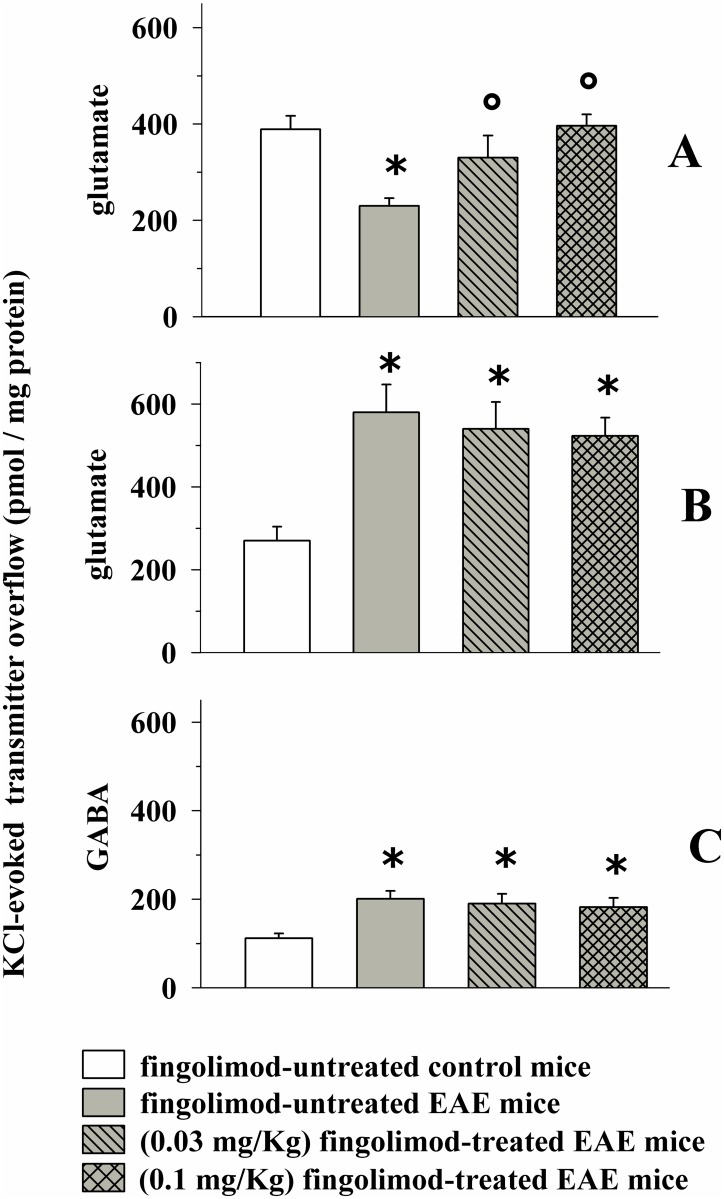
Fig 6. Effect of in vivo different doses of prophylactic fingolimod on the depolarization-evoked exocytosis of endogenous glutamate and GABA from nerve terminals isolated from selected regions of the CNS of control and EAE mice.
Female mice were randomly assigned to the following groups: control mice (empty bar, n = 6 mice); EAE mice (grey bar, n = 8 mice); fingolimod (0.03 mg/kg, n = 8 mice)-treated EAE mice (rising-left hatched grey bar); fingolimod (0.1 mg/kg)-treated EAE mice (cross-hatched grey bar). Fingolimod was administered as described above. At 21 ± 1 d.p.i. mice were sacrificed and cortical (A) and spinal cord (B and C) synaptosomes were isolated to monitor the exocytosis of endogenous glutamate (A and B) and GABA (C) elicited by a mild depolarizing stimulus as previously described. Results are expressed as KCl-evoked overflow of the endogenous aminoacids; data are expressed as pmoles / mg protein and represent the mean ± SEM experiments run in triplicate. * p < 0.05 at least versus control untreated mice; ° p < 0.05 at least versus EAE untreated mice.