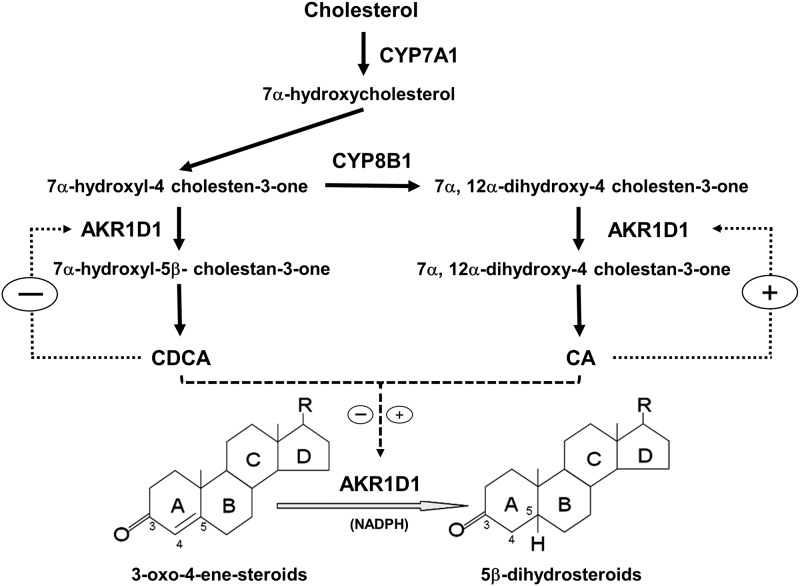
Fig 12. Functions and regulation of AKR1D1 in bile acid synthesis and steroid hormone metabolism.
In the bile acid synthesis pathway, bile acid intermediate 7α-hydroxy-4-cholesten-3-one can take one of the two routes in subsequent steps. If the intermediate is acted upon by AKR1D1, the ultimate product is CDCA. If the intermediate is acted upon by CYP8B1, followed by AKR1D1, the ultimate product is CA. In this study, we demonstrated that CDCA and CA regulated AKR1D1 through a negative and positive feedback mechanism, respectively. In addition to bile acid synthesis, AKR1D1 is also involved in steroid hormone metabolism. 5β-reduction by AKR1D1 is a common transformation and major deactivation pathway for many steroid hormones. Therefore, AKR1D1 plays a critical role in regulating and maintaining the homeostasis of steroid hormones. Thus bile acids crosstalk with steroid hormone signaling pathways through modulating AKR1D1 expression. Plus (+) and minus (-) indicated positive and negative feedback regulation, respectively.