Fig. 5. Overlap between RNA and protein co-expression networks in AD.
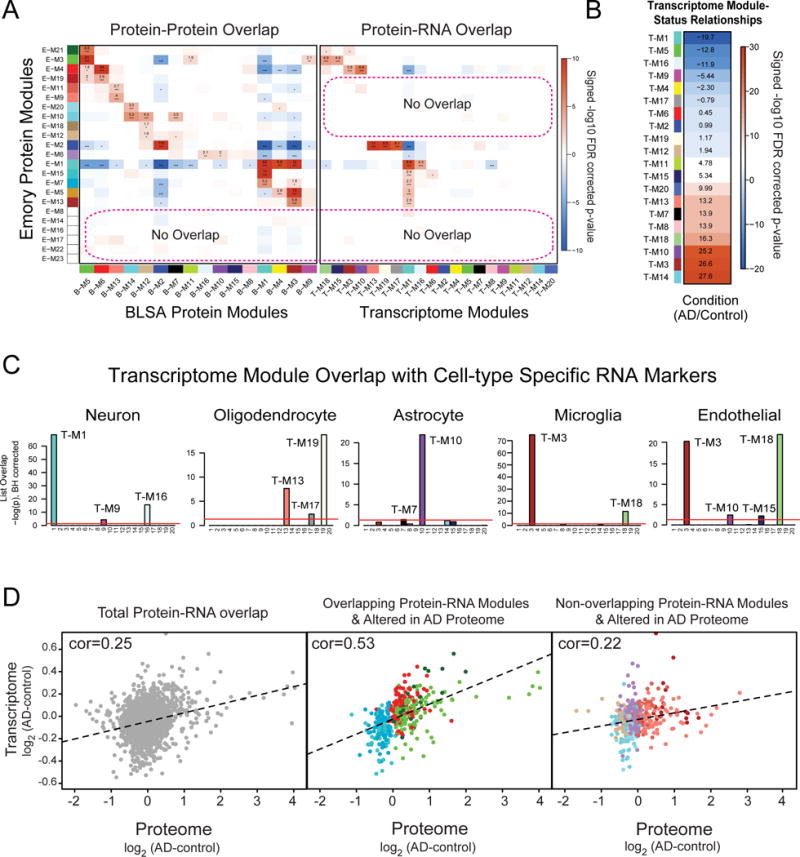
(A) A hypergeometric two-tailed Fisher’s exact test was used to determine which modules shared significant overlap or depletion of module members between the Emory and BLSA proteome networks (left panel) and Emory proteome and RNA networks (right panel). The 23 modules in the Emory case network (x-axis), clustered by module eigenprotein relatedness, were aligned to the 16 modules in the BLSA network (y-axis). Module gene symbol lists showed either significant overlap (red), depletion (blue) or no significant under- or over-representation (white) in protein membership. Numbers are positive signed −log10(FDR-corrected overrepresentation p values) representing degree of significance of overlap; asterisks also represent degree of significance for either positive or depleted comparisons: *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01, ***, p<0.005. (B) The degree of significance related to AD with correlation sign [signed −log10(FDR corrected p value)] is provided for each transcriptome module. Module eigengenes were correlated to AD status and multiple comparisons were accounted for by FDR correction (Benjamini-Hochberg) across modules with significance. (C) RNA modules were found enriched for specific cell type markers (Table S4) including neuronal, oligodendrocyte, astrocyte, microglia and endothelial cells following one-way Fisher’s exact test overlap with cell-type specific transcriptomes. (D) Pearson correlation analysis between all overlapping protein-RNA targets (n=2,406, left panel). Pearson correlation analysis between Protein-RNA targets in Emory modules that overlap with the transcriptome and change in the AD proteome (n=411, middle panel). This included protein modules increased in AD (E-M4, E-M21 and E-M3) that are enriched in astrocyte/microglia/endothelial markers and modules decreased in AD (E-M15 and E-M7) that are enriched with neuronal markers. Pearson correlation analysis between Protein-RNA targets in Emory modules that did not overlap with modules in the transcriptome (n=411, right panel), yet were increased (E-M19, E-M11 and E-M9) or decreased (E-M20, E-M10, E-M6, E-M18 and E-M12) in AD. Genes and cognate proteins were grouped and colored by their Emory protein module membership.
