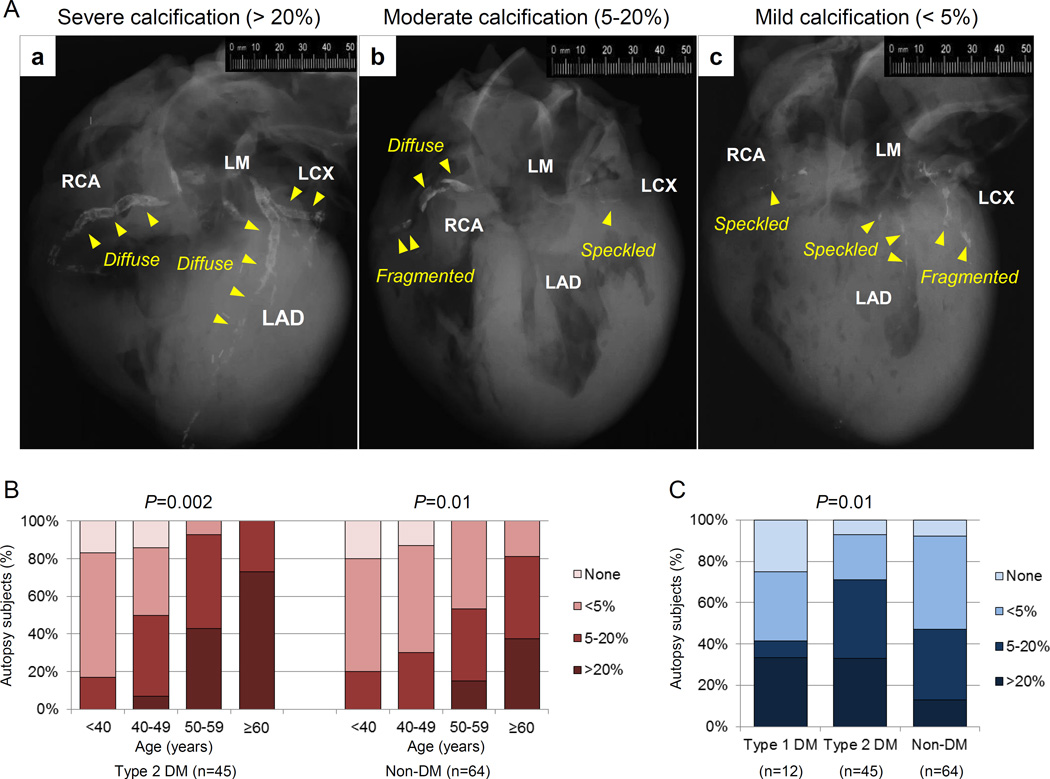
Figure 3.
Coronary artery calcification in sudden coronary death evaluated by post-mortem radiography. (A) Representative post-mortem radiographs showing various patterns of calcification. The severity of calcification was assessed based on the percentage of calcification area: (a) severe artery calcification (>20%), (b) moderate calcification (5–20%), and (c) mild calcification (<5%). Arrows indicate type of calcification (speckled [<2mm in length], fragmented [2–5mm] or diffuse [≥5mm] calcification). (B) Percentage of total calcified area, divided into mild, moderate and severe in sudden coronary death patients with type 2 DM and non-DM stratified by decade. (C) Percentage of total calcified area in sudden coronary death comparing type 1 DM, type 2 DM, and non-DM.