Figure 19.
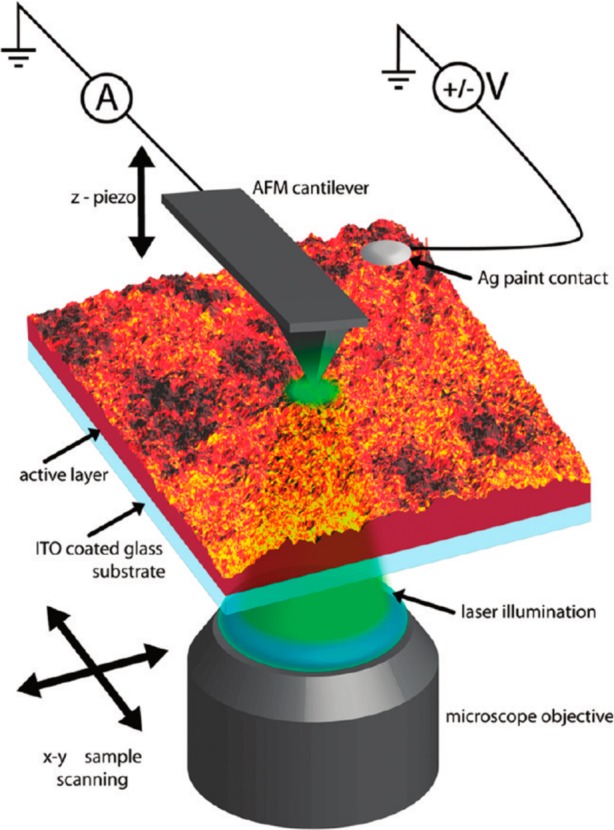
Schematic illustration of a photoconductive AFM setup. Illumination of a sample leads to the generation of excitons that dissociate into charges. These charges are then extracted by the metal AFM tip, which is under bias with respect to the sample substrate. Spatial scanning of the sample (or the tip) allows a 2D photocurrent map to be recorded. Reprinted with permission from ref (198). Copyright 2010 American Chemical Society.
