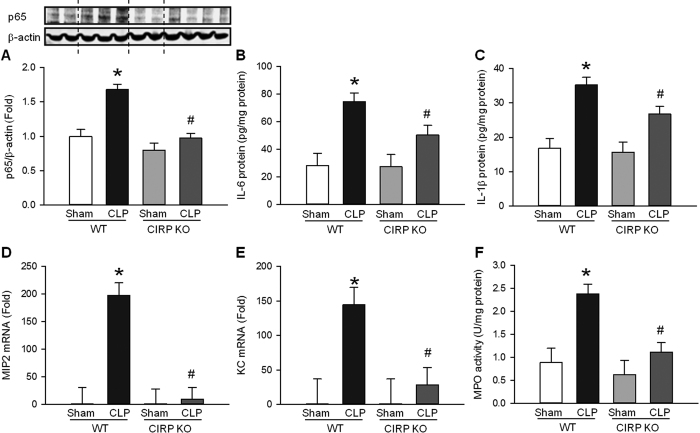
Figure 5. CIRP increases NF-κB, cytokine, and chemokine expression, and neutrophil infiltration in ALI.
(A) Lung levels of NF-κB p65 (WB) were elevated in septic WT mice (*P < 0.05 vs. sham WT mice) and were significantly reduced in septic CIRP KO mice (#P < 0.05 vs. septic WT mice). At 20 h after CLP, the lung protein expression of (B) IL-6 and (C) IL-1β were measured by ELISA, the lung mRNA expression of (D) MIP-2 and (E) KC were measured by real time-PCR, and (F) lung MPO activity was measured by colorimetry. The lung expression of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines, as well as neutrophil infiltration as measured by MPO activity, were elevated in septic WT mice (*P < 0.05 vs. sham WT mice) and were significantly reduced in septic CIRP KO mice (#P < 0.05 vs. septic WT mice). The dotted lines on the WB reflect the groups shown in the histogram below. Data are expressed as last square mean ± SEM. Sample sizes: sham WT = 2–4, CLP WT = 2–8, sham CIRP KO = 2–4, CLP CIRP KO = 4–8.