Figure 7. Schematic diagram of IL-6/sIL-6R differential regulation of varying concentration of RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and activity by osteoclast precursors.
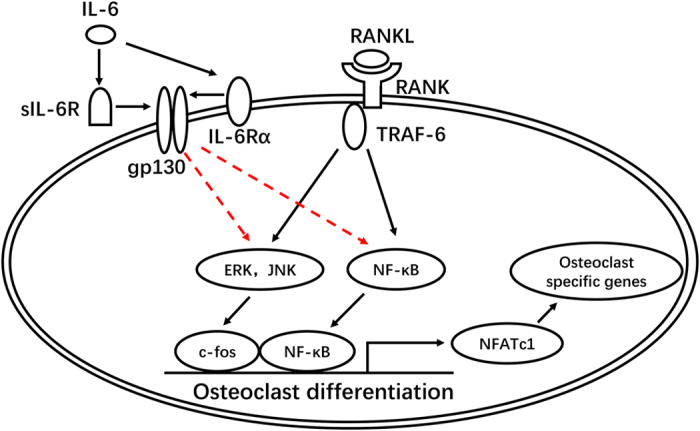
The RANKL-RANK interaction activates downstream signaling pathways such as NF-κB, MAPKs (p38, ERK and JNK) and Akt, which subsequently initiate the expression of osteoclastic transcriptional factors including NFATc1 and c-fos and osteoclast specific genes, thus leading to the commitment to mature osteoclast with potent bone resorptive activity. IL-6/sIL-6R differentially regulate RANKL-induced osteoclast formation via specifically modulating phosphorylation of NF-κB, ERK and JNK in a RANKL concentration-dependent manner, i.e., a stimulatory effect in the condition of low level of RANKL while an inhibitory effect when the level of RANKL remarkably enhanced.
