Fig. 5.
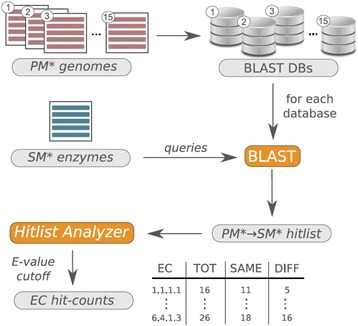
Software architecture for the determination of PM*/SM* homologs. This schema illustrates how the number and the enzyme function of PM* homologs was determined for SM* enzymes. For each of the 15 species listed in Table 1, the genome was downloaded from KEGG and the functional assignment was supplemented by using InterPro and other databases. Subsequently, a BLAST database (DB) was built for each of the genomes. The sequences of the SM* enzymes deduced from the chosen BGCs were then BLASTed against all 15 databases. All BLAST hits were stored in PM* → SM* hitlist that contained all PM* → SM* pairs. Based on the chosen E-value cutoff, our program Hitlist Analyzer selected those hits that both had assigned an EC number and compiled the output table EC hits-counts. This table contained for each EC number the number of PM* hits (TOT) and the number of PM* hits having assigned the same (SAME) and a different (DIFF) EC number. These raw data were further processed to determine frequencies and related parameters for EC numbers, subdivisions, and classes
