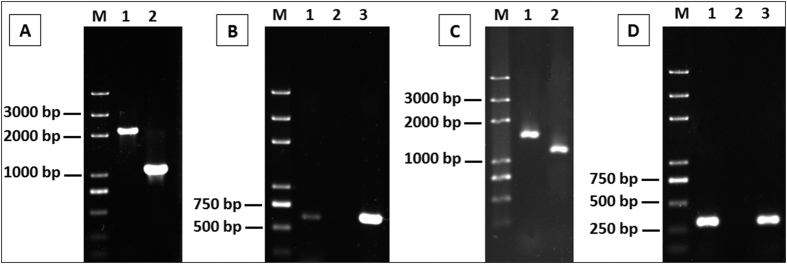
Figure 2.
(A,B) Diagnostic PCR confirming the deletion of aioE to create mutant strain GW4-ΔaioE and complementation to create GW4-ΔaioE-C. (A) PCR amplicons using primers PaioE-1F and PaioE-2R. (B) PCR amplicons using primers IaioE-F and IaioE-R. (C,D) Diagnostic PCR confirming the deletion of cytC to create mutant strain GW4-ΔcytC and complementation to create GW4-ΔcytC-C. (C) PCR amplicons using primers PcytC-1F and PcytC-2R. (D) PCR amplicons using primers IcytC-F and IcytC-R. For panels (A and B): Lane 1, strain GW4, lane 2, aioE gene knock-out strain GW4-ΔaioE and lane 3, the complemented strain GW4-ΔaioE-C. For panels (C and D): Lane 1, strain GW4, lane 2, cytC gene knock-out strain GW4-ΔcytC and lane 3, the complemented strain GW4-ΔcytC-C. M, the molecular weight marker (DL 2000 plus). Amplicon identities were confirmed by DNA sequencing.